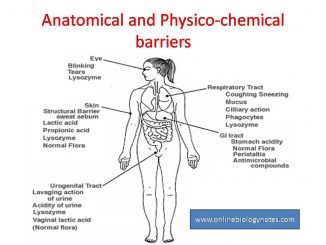
Anatomical and Physico-chemical barriers of immune system
Anatomical and Physico-chemical barriers of immune system Anatomical barriers Skin and mucus membrane are the examples of anatomical barriers that provides immunity. Skin and mucus […]

Anatomical and Physico-chemical barriers of immune system Anatomical barriers Skin and mucus membrane are the examples of anatomical barriers that provides immunity. Skin and mucus […]
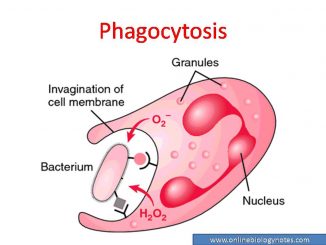
Phagocytosis or Phagocytic barrier of immune system Phagocytosis is an important defense mechanism of host to provide immunity. Most of the bacteria that enter into […]
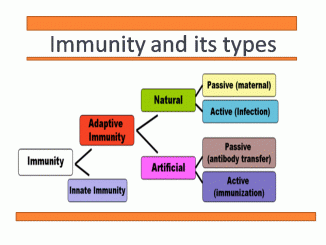
Immunity and its types: Innate and Acquired immunity Immunity is derived from Latin word “immunis” which means free from burden. In this case burden refers […]
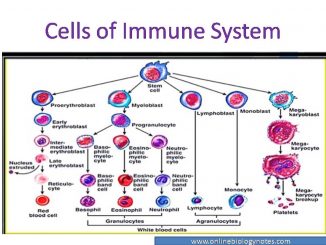
Cells of immune system: Lymphocytes, phagocytic cell, granulocytes and dendritic cells WBCs are the principle cells of immune system formed hematopoietic stem cell by the […]
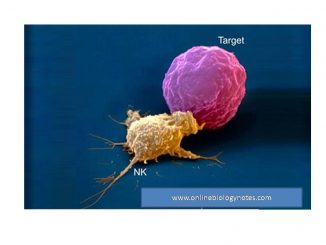
Natural killer (NK) cell Natural Killer (NK) cells are large granular lymphocytes (LGL) present in small proportion in spleen and peripheral blood. Unlike T-cell and […]
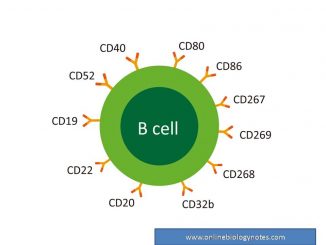
B- lymphocytes: surface receptor and functions The name B-cell is derived from its site of maturation and differentiation in Bursa of fabricius in Birds. In […]
T-lymphocyte: types and functions T-cells originate in bone marrow and mature and differentiate in thymus. The name T- cells is derived from its site of […]

Difference between innate and acquired immunity Point of distinction Innate immunity Acquired immunity Definition Immunity with which an individual is born Immunity which […]

Virulence factors of bacteria; microbial virulence factors Virulence factor refers to the components or structure of microorganism that helps in establishment of disease or infection. […]
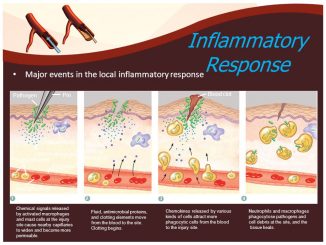
Inflammation or Inflammatory barrier of immune system Inflammation is an important defense mechanism of host to prevent infection. It is induced in response to tissue […]
Copyright © 2024 | WordPress Theme by MH Themes