
Paper chromatography – Principle, Procedure, types and applications
Principle of paper chromatography: This technique is a type of partition chromatography in which the substances are distributed between two liquids, i.e., one is the […]

Principle of paper chromatography: This technique is a type of partition chromatography in which the substances are distributed between two liquids, i.e., one is the […]

Pectinase enzyme: Pectinase is the collective term for row of enzyme that are able to breakdown or transform pectins. Pectinase is a general form for […]

Chitinase: Chitinases are hydrolytic enzymes with the size ranging from 20kDa to about 90kDa. Chitinase present in wide range of organisms such as bacteria, fungi […]

Enzymes- Introduction Enzymes are proteins which catalyzes specific biochemical reactions is a very efficient manner. Enzymes can be produced by different types of micro-organisms, plant […]

Genus: Shigella Dysentery is a clinical condition of multiple etiology characterized by frequent passage of blood-stained mucopurulent stool. The causative agent of bacillary dysentery (Disease […]

Amylase enzyme: Starch, a glucose polymer is one of the most widely available plant polysaccharides which is hydrolysed by an enzyme called amylase. One of […]

Genus Salmonella: Salmonella is an enterobacteria (fermentative, facultative anaerobes, oxidase -ve, gram -ve rods, catalase +ve). Motile (generally), aerogenic, non-lactose fermenting urease -ve, citrate +ve, […]

Single cell protein: The dried cells of micro-organisms (Algae, Bacteria, Actinomycetes and fungi) used as food or feed are collectively called microbial protein. The term […]

What is primary cell culture? The stage of the culture after isolation of the cells but prior to the first sub culture after which it […]
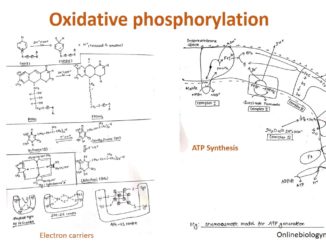
Oxidative phosphorylation: Reducing equivalent NADH, FADH2 generated during glycolysis and the link between glycolysis and Kreb’s cycle are used to synthesize ATP by a process […]
Copyright © 2024 | WordPress Theme by MH Themes