
Adenovirus: Structure and genome, Replication, Pathogenesis, Infection, laboratory diagnosis, Prevention and Treatment
I. Structure
Adenoviruses are the group of medium sized, non enveloped ds DNA virus that share common complement fixing antigen.
Size: 70-90 nm in diameter
Shape: Icosahedral
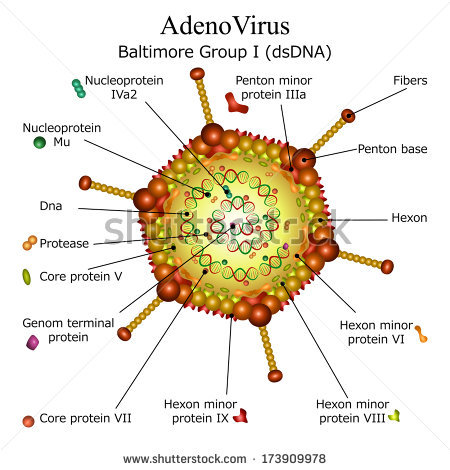
Genome:
- Linear ds DNA molecule of 26-45 kbp long and DNA have inverted terminal repeats of approximately 100bp at both ends.
- Each DNA strand is covalently attached to virus encoded protein at 5’ end
Capsid:
- Capsid is Icosahedral in shape and is composed of 292 capsomeres with 20 triangular facets and 12 vertices.
- The capsid consists of 240 hexons and 12 pentons.
- Each pentons unit consists of a penton base anchored in capsid and a projection (fiber or knob) with a knot at distal end. Thus the virion looks like space vehicle.
- The projection or fiber helps to bind Adenovirus to host cell.
- The fiber contains viral attachment protein which acts as hemagglutinin.
- Penton base carries a toxin like activity that causes cytopathic effect (CPE) on host cell.
II. Replication of Adenovirus
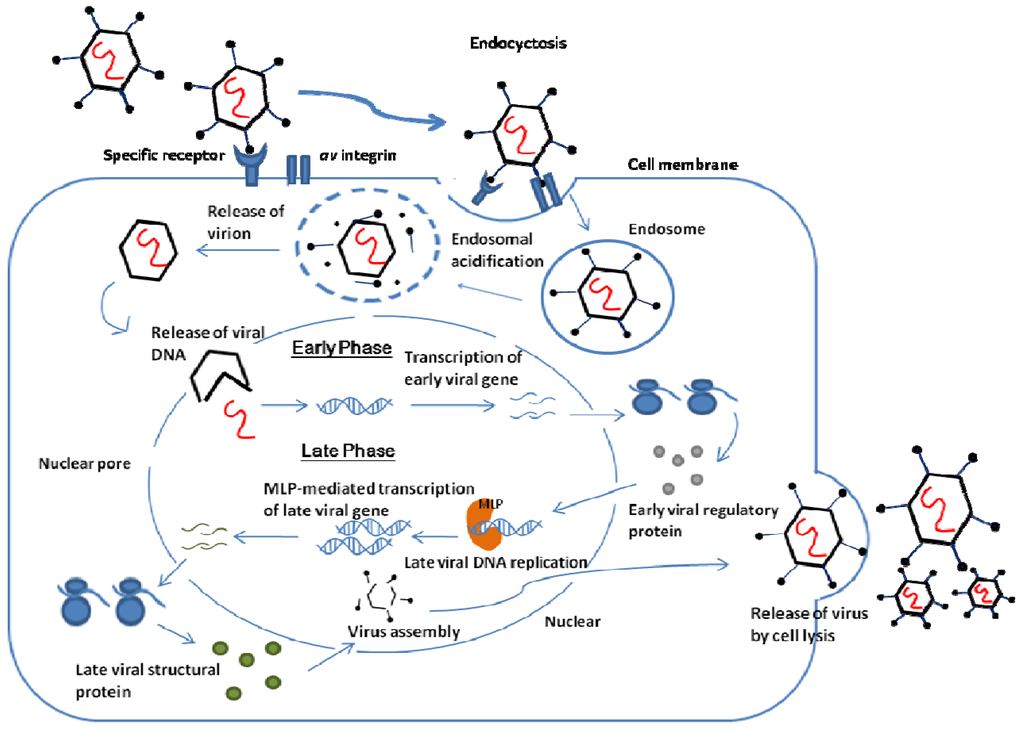
Step I: Attachment and entry
- Adenovirus attaches to the host cell via its fiber structure to Coxsackie and Adenovirus receptor (CAR) receptor on host cell.
- The attachment of fiber to its receptor on host cell is followed by interaction of penton base with cellular integrin which promote receptor mediated internalization.
Step II: Uncoating
- The virus is internalized into clathrin coated endosome and the high pH of endosome helps in uncoating of virus
- Transport of viral DNA into nucleus
- The viral nucleocapsid is transported from cytosol to nucleus by the help of microtubules.
Step III: Early Transcription
- It is the early event in viral replication, and occurs before viral DNA synthesis begins.
- It is the preparatory phase in which transcription of viral DNA occurs to mRNA (early transcript).
- Early transcript undergoes translation to produce about 20 different early proteins. These early proteins induces host cell to enter into S-phase of cell cycle and to create condition favorable for viral replication.
Step IV: DNA replication
- Viral DNA replication takes place in nucleus.
- The viral encoded protein at 5’ end of viral DNA strand acts as primer for initiation of viral DNA synthesis.
- Late event begins concomitantly with onset of viral DNA synthesis.
Step V: Late Transcription and translation
- A large single primary transcript is synthesized from virus DNA which spliced into 18 fragments and each fragment acts as mRNA and are transported to cytoplasm.
- In the cytoplasm, translation occurs and viral structural proteins are synthesized.
Step VI: Viral morphogenesis and release
- Morphogenesis of Adenovirus occurs inside nucleus.
- Viral DNA then gets packaged into preformed capsid forming mature virus particle.
- Mature virus particles are stable, infectious and resistant to nuclease enzyme of host cell.
- Adenovirus infection does not lyse the host cell.
- Mature virus is then release from host cell by budding.
III. Mode of transmission of Adenovirus
- Adenovirus infection transmits from person to person directly by-
- Aerosol droplets ( respiratory route)
- Faeco-oral route
- Contaminated fingers to infects conjunctiva
- Contaminates fomites
IV. Pathogenesis
- Adenovirus can infects and replicates in epithelial cells of respiratory tracts, gastro-intestinal tracts, urinary bladder and eyes.
- After entry of Adenovirus inside human body, it can multiply in epithelial cells of conjunctiva, pharynx or small intestine according to mode of entry and then spreads to regional lymph nodes.
- Usually Adenovirus does not spread beyond regional lymph node.
- Adenovirus produces three types of infections:
1. Lytic infection
- Virus actively replicates inside host cell producing lytic effects causing cell death and releases progeny viruses.
- After local infection viruses may spread to visceral organs.
2. Latent infection:
- Adenovirus has a property to become latent in lymphoid organs such as tonsil and payer’s patches.
- Latent infection can be reactivated in person with underlying immunity.
3. Oncogenic transformation:
- Certain Adenovirus (group A and B) can transform host cell into cancerous cell by integrating viral DNA into host DNA.
- Although the oncogenicity has not been seen in Human infection.
V. Adenovirus infection and diseases
- Adenovirus primarily infects children and accounts less in adults.
- Most Adenovirus infections are mild and self limiting.
1. Respiratory diseases:
- Pharyngitis: Adenovirus is major causes of non-bacterial pharyngitis.
- Pneumonia: Adenovirus 3 and 7 are associated with pneumonia.
- Acute respiratory disease: fever, rhinorrhoea, cough , sore throat that lasts for 3-5 days.
- Pharyngoconjunctival fever: Fever, red eyes, sore throat that occurs primarily in school going children.
2. Eye infection:
- Keratoconjunctivitis: It is highly contagious and characterized by photophobia, tearing, pain and inflammation of conjunctiva.
- Gastro-intestinal infection
- Intangible gastroenteritis:I It is characterized by fever and watery diarrhoea.
3. Other infections:
- Pertussis like symptoms in children
- Musculoskeletal disorder
- Genital infection
- Skin infection
VI. Lab diagnosis
- Specimens:
- Depends upon nature of infections.
- Throat swab, nasopharyngeal aspirates, conjunctival aspirates, conjunctival swab, urine, stool, blood, body fluids
- Microscopy: Electron microscope
- Antigen detection: ELISA, DFA test
- Serology or antibody detection
- Molecular technique: PCR, DNA probe
- Virus culture: cell line culture
VII. Prevention from Adenovirus infection
- Maintain personal hygiene
- Wash hands often with soap and water
- Avoid direct personal contact with diseased person
- Cover mouth and nose while coughing and sneezing
- Avoid touching eye, nose or mouth without washing hands
- Visit Hospital in case of any symptoms
VIII. Treatments
- Not specific
- Some antiviral drugs such as Ganciclovir, Vidarabine, Ribavirin, Cidofovir
