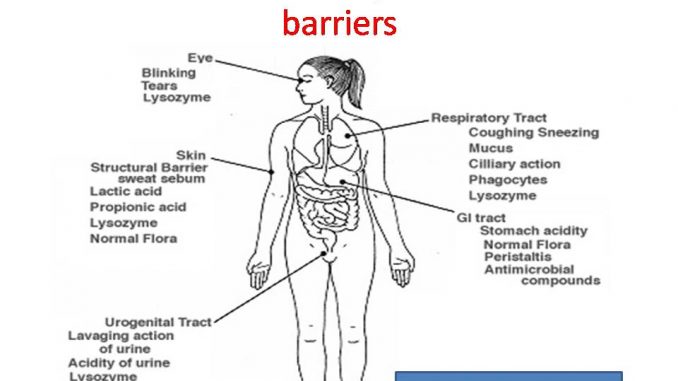
Anatomical and Physico-chemical barriers of immune system
Anatomical barriers
Skin and mucus membrane are the examples of anatomical barriers that provides immunity.
Skin and mucus membrane:
- Skin consists of two distinct layer; a thin outer layer called epidermis and thick inner layer called dermis.
- Epidermis consists of mostly dead cell filled with keratin. Dermis is composed of connective tissue, hair follicle, sebaceous gland and sweat gland.
- Skin provides first line of defense by preventing entry of microorganisms. However skin may be penetrated by injury or insects.
- Below skin, the mucus membrane prevents the entry of microorganism to the body. And also it secrets mucus that entraps microorganisms.
Anatomical barriers provide immunity by following ways.
- At first skin and mucus membrane prevent entry of microorganism into host body by mechanical separation. For example, Skin surrounds the host body from external and mucus membrane surrounds the body tracts.
- They also have mechanism to kill the pathogen before entry to body. For example; lysozyme, acidic pH, sebum, high salt concentration in sweat are antimicrobial agents found in skin and mucus membrane.
- Skin and mucus membrane provides first line of defense against microorganism as they are first component to encounter with microorganism.
Physico-chemical barriers
- Physicochemical barrier includes physiological barrier and chemical barrier.
- Physiological conditions of body such as normal body temperature, normal body pH etc provides immunity.
- Some species are resistant to certain disease simply because of their higher body temperature. For example, mammals are susceptible to anthrax but birds are resistant to anthrax. It is because Bacillus anthracis are killed by higher body temperature of birds (39°C).
- Similarly, body pH also provides immunity. For example acidity of stomach kills most of the ingested bacteria and provides immunity. In infants stomach is less acidic. This is the reason why infants suffer more from gastrointestinal disturbance than adults.
- Chemical barriers include various antimicrobial chemicals found in body fluids. For examples, Lysozyme found in tear and mucus kills many Gram +ve bacteria.
- Interferon found in blood and lymph kills viruses. Other antimicrobial chemicals found in body fluids include complement protein, collectins, etc.
