B- lymphocytes: surface receptor and functions
- The name B-cell is derived from its site of maturation and differentiation in Bursa of fabricius in Birds. In adult human B- cell originates and mature in Bone marrow.
- Morphologically B- cells are indistinguishable from T-cells. B-cells are identified by their surface protein ie. Immunoglobulin or antibody which serves as receptor for antigen.
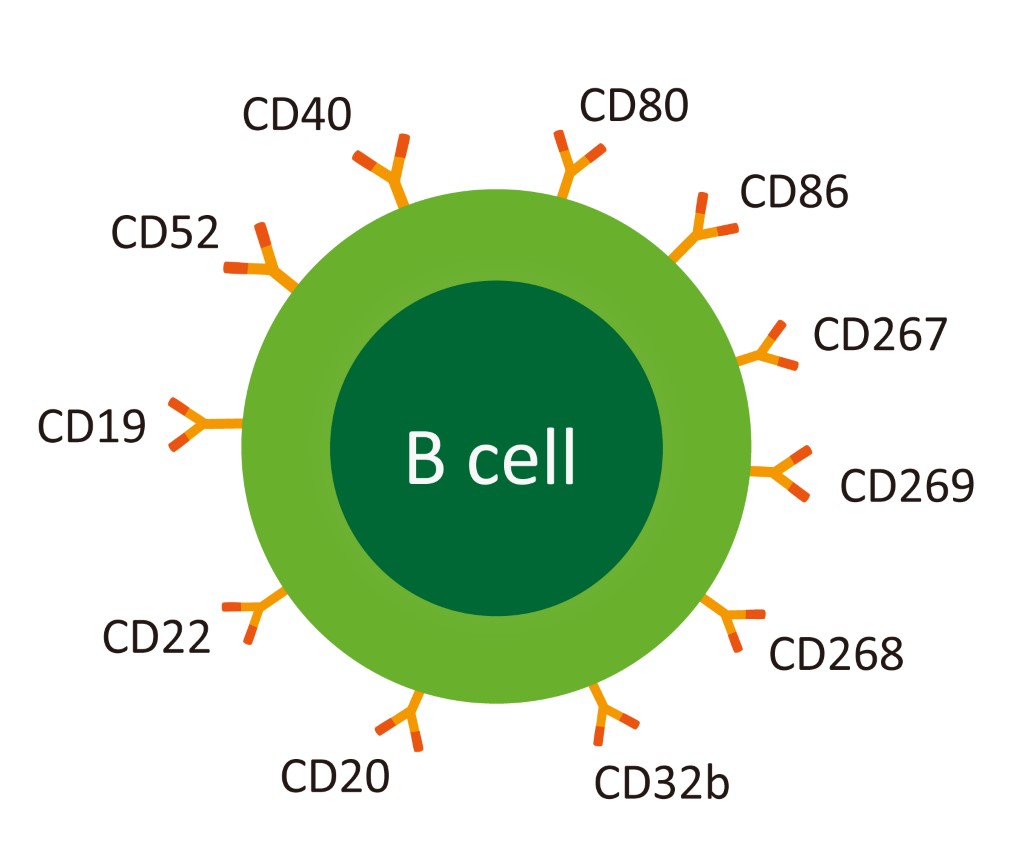
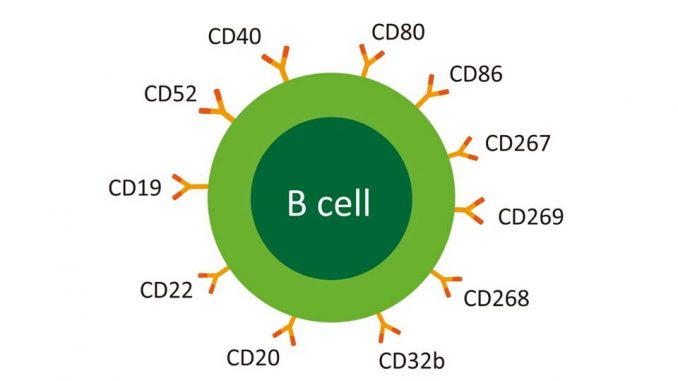
Other surface receptor molecules on B-cells are;
- B220 (CD45): marker for B-cells and their precursor
- MHC-II: permits B-cells to function as APC.
- CR1 (CD35) and CR2 (CD21): complement receptor
- FcγRII (CD32): receptor for IgG antibody
- CD40: interacts with CD40 ligands on surface of TH cells.
- B7-1 (CD80) and B7-2 (CD86): interacts with CD28 and CTLA-4 on TH cells.
Immunological functions of B-cells:
- Antibody production against specific target antigen
- Acts as APC and Present antigen to t-lymphocytes
- Provides signal for T – cell activation
