
Bacterial Cell wall: Structure, Composition and Types
- Cell wall is an important structure of a bacteria. It give shape,rigidity and support to the cell.
- On the basis of cell wall composition, bacteria are classified into two major group ie. Gram Positive and gram negative.
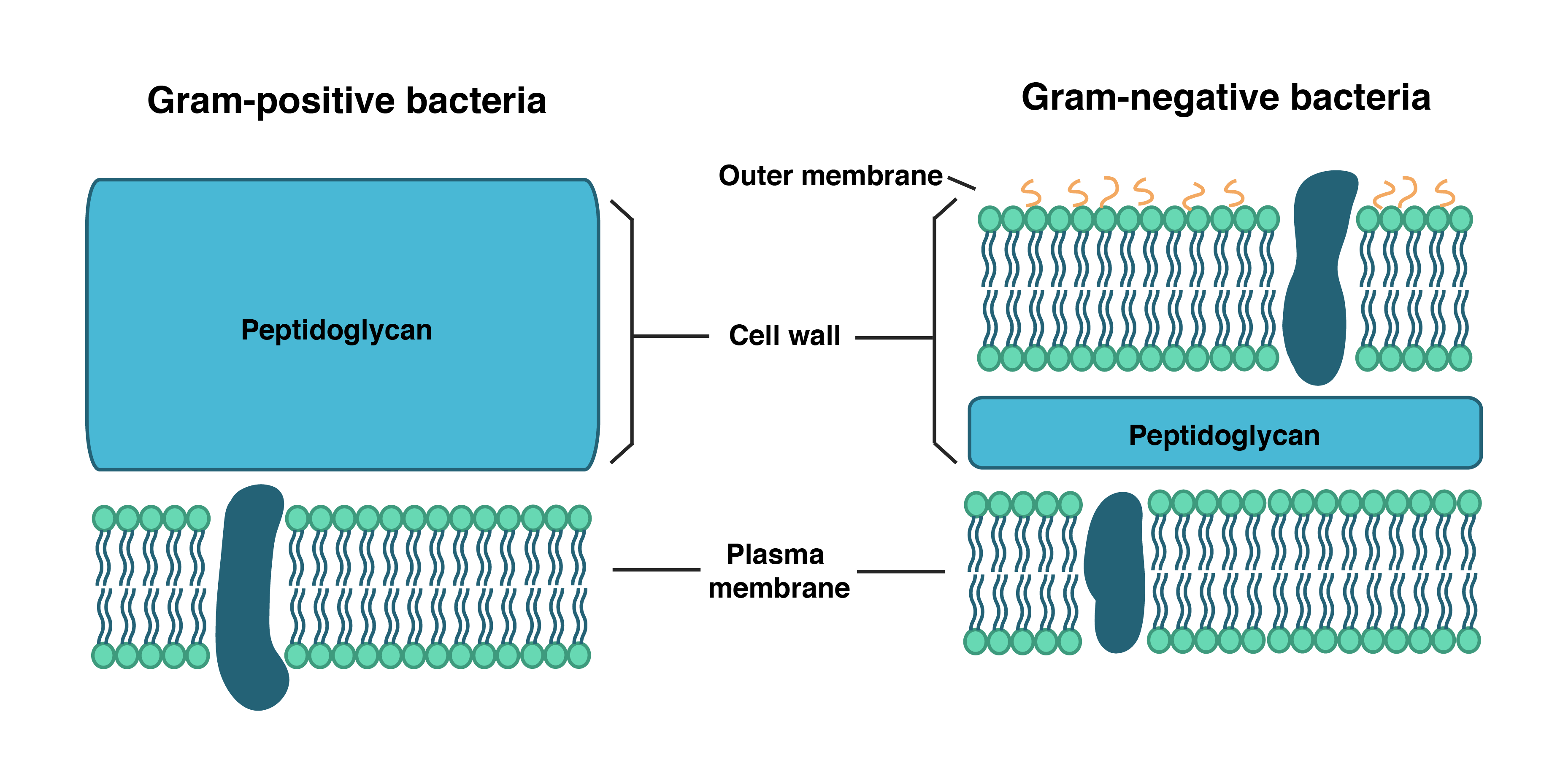
Types of cell wall
1. Gram positive cell wall
Cell wall composition of gram positive bacteria.
- Peptidoglycan
- Lipid
- Teichoic acid
2. Gram negative cell wall
Cell wall composition of gram negative bacteria
- Peptidoglycan
- Outermembrane:
- Lipid
- Protein
- Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)
Composition of cell wall:
1. Peptidoglycan:
- Peptidoglycan is porous cross linked polymer which is responsible for strength of cell wall.
- Peptidoglycan is composed of three components.
- Glycan backbone
- Tetra-peptide side chain ( chain of 4 amino acids) linked to NAM
- Peptide cross linkage
- Glycan backbone is the repeated unit of N-acetyl muramic acid (NAM) and N-acetyl glycosamine (NAG) linked by β-glycosidic bond.
- The glycan backbone are cross linked by tetra-peptide linkage. The tetra-peptide are only found in NAM.
- More than 100 peptidoglycan are known with the diversity focused on the chemistry of peptide cross linkage and interbridge.
- Although the peptidoglycan chemistry vary from organism to organism the glycan backbone ie NAG-NAM is same in all species of bacteria.
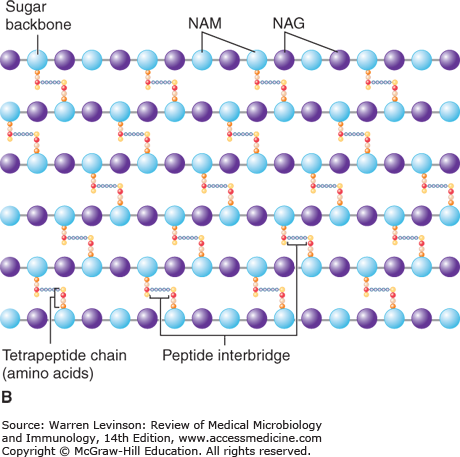
The aminoacids found in tetra-peptide are-
- L-alanine: 1st position in both gm+ve and gm-ve bacteria
- D-glutamic acid: 2nd position
- D-aminopimelic acid/ L-lysine: 3rd position (variation occurs)
- D-alanine: 4th position
Peptide cross linkage in Gram positive and Gram negative bacteria
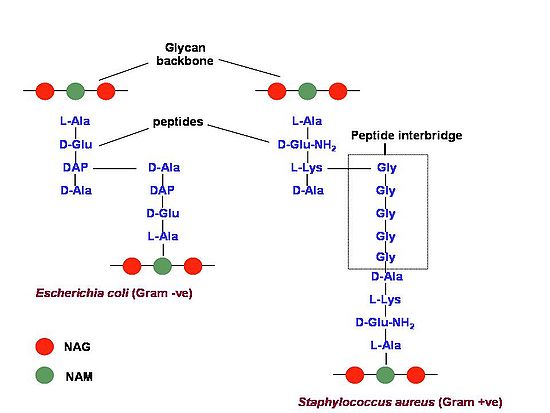
- In gram negative bacteria, peptide cross linkage occur between Diaminopamilic acid (3rd position) of one glycan back bone and D-alanine of adjacent glycan back bone.
- In gram positive bacteria, peptide cross linkage occur by peptide interbridge. The type and number of aminoacids in interbridge vary among bacterial species.
2. Teichoic acid:
- Teichoic acid is water soluble polymer of glycerol or ribitol phosphate.
- It is present in gram positive bacteria.
- It constitutes about 50% of dry weight of cell wall.
- It is the major surface antigen of gram positive bacteria.
3. Outer membrane
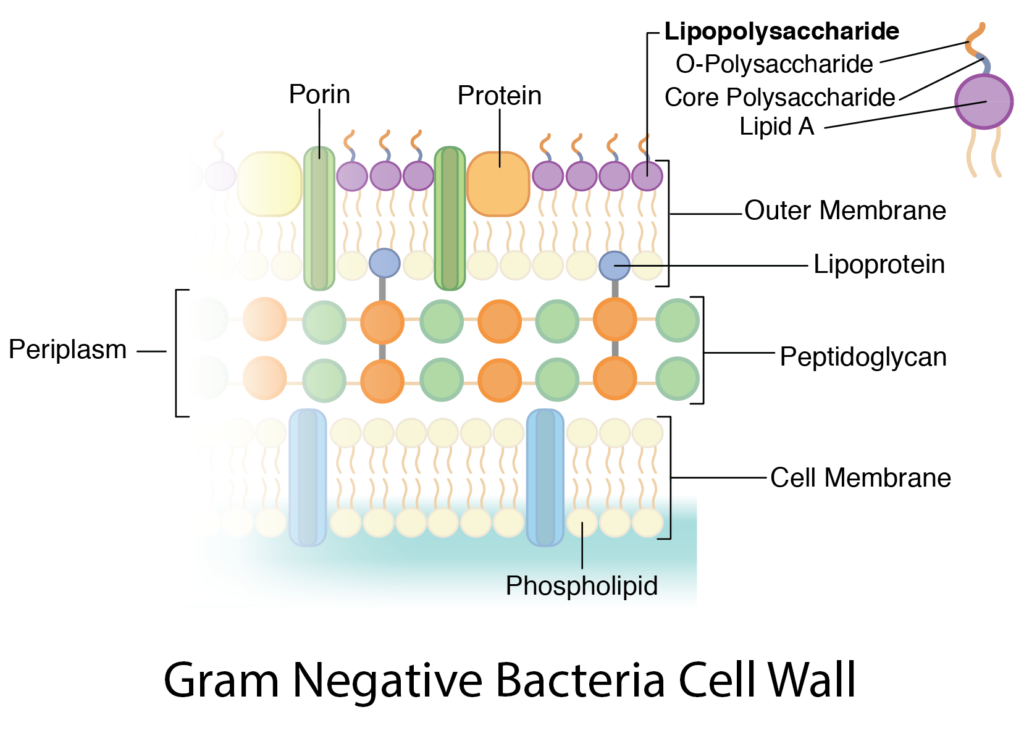
Figure: Outer membrane in cell wall of gram negative bacteria
- It is an additional layer present in gram negative bacteria.
- It is composed of lipid bilayer, protein and lipopolysaccharide (LPS) layer
Function of outer membrane:
- Structure component of gram-ve cell wall
- LPS is an endotoxin produced by gram –ve bacteria
- Lipid-A is antigenic
4. LPS
- LPS is attached to outer membrane by hydrophobic bond. LPS is synthesized in cytoplasmic membrane and transported to outer membrane.
- LPS is composed of lipid-A and polysaccharide.
- Lipid-A: it is phosphorylated glucosamine disaccharide.
- Polysaccharide: it consists of core-polysaccharide and O-polysaccharide.
Gram positive bacteria
Micrococcus
Staphylococcus
Streptococcus
Leuconostoc
Gram negative bacteria
E. coli
Salmonella
Klebsiella
Shigella
Pseudomonas
