
Bacterial Flagella: structure, types and function
- Flagellum (singular) is hair like helical structure emerges from cell wall and cell membrane
- It is responsible for motility of the bacteria
- Size: thin 15-20nm in diameter.
- Single flagella can be seen with light microscope only after staining with special stain which increase the diameter of flagella.
Structure of flagella: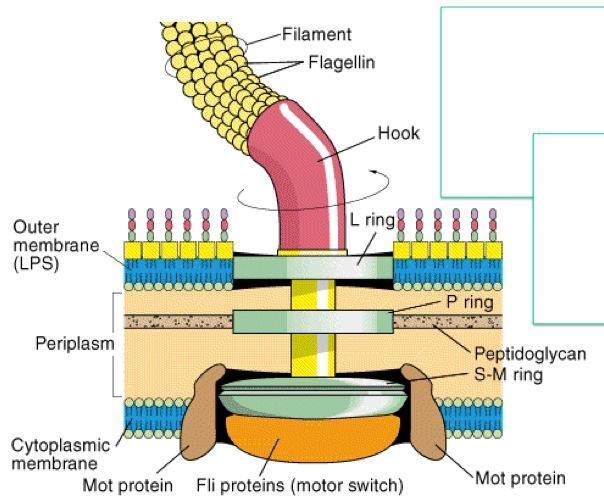
- Flagella is not straight but is helical.
- It is composed of flagellin protein (globular protein) and known as H antigen.
- Flagella has three parts. Basal body, Hook and filament
Basal body:
- it is composed of central rod inserted into series of rings which is attached to cytoplasmic memvbrane and cell wall.
- L-ring: it is the outer ring present only in Gram -ve bacteria, it anchored in lipopolysaccharide layer
- P-ring: it is second ring anchored in peptidoglycan layer of cell wall.
- M-S ring: anchored in cytoplasmic membrane
- C ring: anchored in cytoplasm
Hook:
- it is the wider region at the base of filament
- it connects filament to the motor protein in the base
- length of hook is longer in gram +ve bacteria than gram –ve bacteria
Filament:
- it is thin hair like structure arises from hook.
Types of flagella
On the basis of arrangement
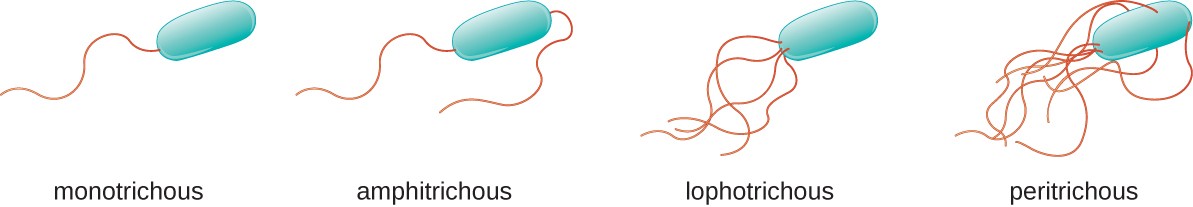
1. Monotrichous:
- presence of single flagella in one end of cell.
- examples; Vibrio cholera, Pseudomonas aerogenosa
2. Lophotrichous:
- presence of bundle of flagella in one end of cell.
- example: Pseudomanas fluroscence
3. Amphitrichous:
- presence of single or cluster of flagella at both end of cell.
- example; Aquaspirillium
4. Peritrichous:
- presence of flagella all over the cell surface.
- example; E.coli, Salmonella, Klebsiella
5. Atrichous:
- absent of flagella.
- example; Shigella
Function:
Flagellar motility:
- At the base surrounding the inner ring (M-S and C ring) there is a series of protein called Mot protein.
- A final set of protein called Fli protein function as motor switch. The flagella motor rotates the filament as a turbine causing movement of the cell in the medium.
- The movement of flagella results from rotation of basal body which is similar to the movement of the shaft of an electric motor.
- A turning motion is generated between S-ring and M ring. S-ring acts as starter while M ring acts as roter.
- The basal body as a whole give a universal joint to the cell and allows complete rotation of hook and filament.
- Flagella moves the cell by rotating the flagella about the basal body. Rotation of flagella is either clockwise or anticlockwise.
