Concept of Bioremediation:
- Bioremediation is a biotechnical process which involves the removal of complex material or contamination by degrading environmental pollutants using living micro-organisms.
- It is a technique to eliminate pollutants from the environment, restoring contaminated sites and avoiding future pollution.
- Bioremediation activity relies on natural capacity of micro-organisms to degrade organic compounds.
- The ability of micro-organisms could be enhanced by providing optimum growth conditions to micro-organism or by employing the genetically modified micro-organisms (GMMs). This technology has been implemented to eradicate environmentally hazardous chemicals and detoxify them into nontoxic forms.
- Micro-organisms play vital role in bioremediation, several members of microbial group like algae, fungi and bacteria are able to solubilise, transport and deposit the metals, and detoxify dyes and complex chemicals.
- The toxic waste materials are present in form of vapour, liquid or solid phases; therefore, bioremediation technology differs depending upon nature of toxic material.
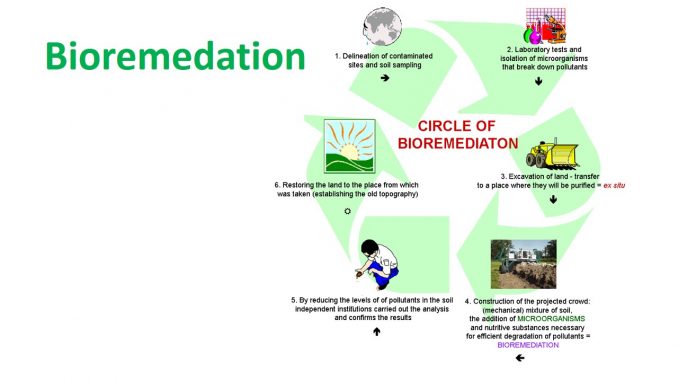
Types of bioremediation:
- Basically there are two methods of bioremediation based on removal and transportation of wastes for treatment:
Advantages of bioremediation:
- Natural process:
- Bioremediation being a natural process is accepted by the public as waste treatment method for contaminated material such as soil.
- Microbes capable of degrading the contaminant, increase in numbers and produce harmless products.
- The residues for the treatment are normally harmless products such as carbon dioxide, water, and cell biomass.
- Complete destruction:
- Bioremediation is employed for the complete destruction of a wide variation of contaminants.
- Many hazardous compounds can be transformed to non-toxic products. This reduces the chance of future responsibility related with treatment and disposal of contaminated material.
- Bioremediation can be performed on site treatment, without causing a major disturbance of normal activities. This removes the requirement to transport huge quantities of waste off site and thus decreases potential hazards to human health and the environment that can arise during transportation.
- Economic process:
- Bioremediation is cost effective in comparison to other methods that are used for removal of hazardous waste.
Limitations of bioremediation:
- Limited up to biodegradable compounds:
- Bioremediation is limited to biodegradable compounds.
- This method is prone to rapid and complete degradation.
- Products of biodegradation may be more lasting or toxic than the parent compound.
- Specificity:
- Biological processes are largely specific.
- The presence of metabolically capable microbial populations, suitable environmental growth conditions, and adequate levels of nutrients and contaminants are the important sites factors required for successful bioremediation.
- Scale up limitation:
- It is tough to scale up from bench and pilot scale studies to full scale field operations.
- Technological advancement :
- Research is required to develop and advance bioremediation technologies that are appropriate for sites with complex mixtures of contaminants that are not evenly distributed in the environment i.e. it may be present as solids, liquids, and gases.
- Tedious process:
- Bioremediation consumes much time compared to other treatment options, such as excavation and removal of soil from contaminated site.
- Regulatory uncertainty:
- We are not sure to say that remediation is 100% completed, as there is no known definition of clean.
- Due to that performance evaluation of bioremediation is complex, and there is no fixed endpoint for bioremediation treatments.
