
Pulmonary air volume and capacities
Pulmonary air volume and capacities In normal quiet breathing there are about 15 complete respiratory cycles per minute. The amount of air exchanged during breathing […]

Pulmonary air volume and capacities In normal quiet breathing there are about 15 complete respiratory cycles per minute. The amount of air exchanged during breathing […]

Oxygen dissociation curve The effect of carbon dioxide and acidity favor the formation of Oxyhaemoglobin at low concentration of CO2 and H+ ion and causes […]

Chloride shift/Hamburger phenomenon The greater proportion (70%) of carbon dioxide is transported in the form of bicarbonates. The CO2 reacted with the water of the […]

Entire physiology of respiration involves following steps Breathing or pulmonary ventilation External respiration Transport of O2 to tissue Internal respiration Transport of CO2 from tissue […]

Physiology of digestion Digestion: Digestion is the process of gradual break down of foods that we eat in a soluble form suitable for absorption. For […]

Salivary gland The human salivary gland is an exocrine gland. The salivary gland includes- the paired parotid, submandibular, and sublingual glands. The major function of […]

Blood: composition, properties and functions Blood is a liquid connective tissue that contains cellular elements (blood cells) and fluid matrix (plasma). Blood helps in the […]
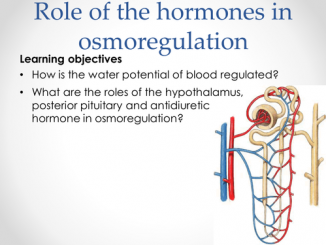
Role of ADH, Renin-Angiotensin and Aldosterone in Osmoregulation 1. ADH (Anti-diuretic Hormone) Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) has the primary role in osmoregulation by controlling the amount […]
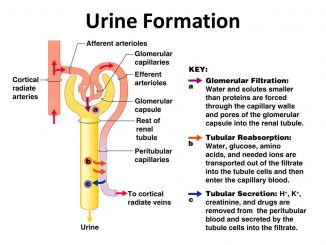
Physiology of Urine formation There are three stages involved in the process of urine formation. They are- 1. Glomerular filtration or ultra-filtration 2. Selective reabsorption […]
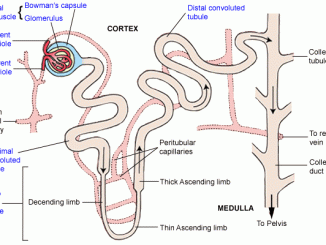
Nephron-Structural anatomy and types Histologically, each kidney is composed of approximately 1 million of Uriniferous tubules or nephron. Nephron is the structural and functional unit […]
Copyright © 2024 | WordPress Theme by MH Themes