
Fatty acids: Definition and Types of fatty acid
Fatty acids: Definition and Types of fatty acid Fatty acids are carboxylic acids with hydrocarbon chain ranging from 4 to 36 caarbon atom ie. C4 […]

Fatty acids: Definition and Types of fatty acid Fatty acids are carboxylic acids with hydrocarbon chain ranging from 4 to 36 caarbon atom ie. C4 […]
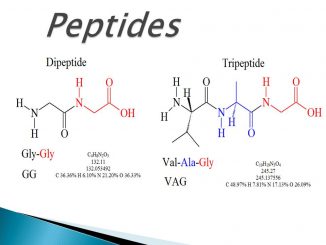
Peptide: Types and functions Peptide (peptide bond) is amide linkage formed by the reaction between α-carboxyl group of one amino acid and α-amino group of […]
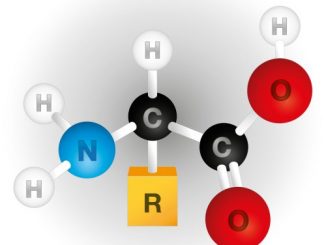
Amino acids: Characteristics and Classification of amino acids Amino acids are carboxylic acid in which α-carbon is attached to the amino group as well as […]

Difference between glycolysis and pentose phosphate pathway Characteristics Glycolysis Pentose phosphate pathway Types of pathway Major energy yielding pathway for carbohydrate metabolism Biosynthetic […]

Citric acid cycle or Krebs cycle or Tri-carboxylic acid (TCA) cycle Citric acid cycle is a central metabolic pathway for metabolism of carbohydrates, fats and […]

Entner-Doudoroff (ED) pathway This pathway occurs in both aerobic and anaerobic condition Occur in prokaryotes only It occurs in cytoplasm Pyruvate and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate produced from […]

Glyoxylate cycle-steps Glyoxylate cycle occurs in some microorganisms when acetate is sole source of carbon This cycle has two unique enzyme- isocitrate lyase and malate […]

Pentose phosphate pathway (PPP) or Hexose mono-phosphate (HMP) shunt • Pentose phosphate pathway is an alternative pathway to glycolysis and TCA cycle for oxidation of […]

Different Fermentation pathway of bacteria 1. Alcoholic fermentation In this pathway first glucose is converted into Pyruvate by glycolysis. And then alcohol dehydrogenase reduces the […]

Difference between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic translation Translation Prokaryotes Eukaryotes Initiation factor Three (IF3, IF2, IF1) Nine (eIF4F complex; eIF4E, eIF4G,eIF4A) Ribosome 30S and 50S 40S […]
Copyright © 2024 | WordPress Theme by MH Themes