
MRS Broth test: Principle, Composition, Procedure, and Results interpretation
Principle: MRS broth is a medium for the cultivation of lactobacilli and is specifically useful for a number of fastidious strains which is unable to […]

Principle: MRS broth is a medium for the cultivation of lactobacilli and is specifically useful for a number of fastidious strains which is unable to […]

Principle of Optochin susceptibility test: Streptococcus pneumoniae is found generally on respiratory tract and has a hemolytic pattern identical to other alpha-hemolytic streptococci and lactobacilli. […]

Principle of MUG test: About 97% strains of Escherichia coli and organisms as such Salmonella, Shigella, and Yersinia are capable of producing enzyme β-glucuronidase. MUG […]

Principle: Salmonella-shigella (SS) agar is generally employed for the selective isolation and differentiation of Salmonella and Shigella in both clinical and nonclinical samples. However, SS […]

Principle: Haemophilus spp. typically grows on chocolate agar as smooth, flat or convex buff, or slightly yellow colonies. Chocolate agar provides hemin (X factor) and […]

Principle: The phenylalanine deaminase (PDA) test is employed to differentiate among the urea- positive gram-negative bacilli on the basis of the ability of the microorganisms […]

Objective: To check whether the organism is capable of utilizing malonate as sole source of carbon and energy for its growth. To categorize organisms on […]

Principle: Dental caries (tooth decay) is damage to enamel of tooth that develop into tiny holes or openings caused by bacteria. In course of the […]
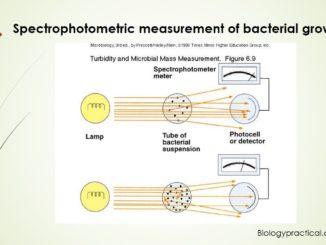
Principle: The quantitative detection of the bacterial population is needed for various studies. There are basically two methods used for the counting of bacterial population […]

Principle: There are various techniques/methodologies for the enumeration (counting) of bacteria in a given sample. A viable cell count permits to detect the number of […]
Copyright © 2024 | WordPress Theme by MH Themes