
Urease test: Objective, Principle, Procedure and result
Urease test: Objective to check whether the organism can produce urease enzyme for the degradation of urea or not. Principle of urease test: Urea is […]

Urease test: Objective to check whether the organism can produce urease enzyme for the degradation of urea or not. Principle of urease test: Urea is […]

Citrate utilization test: Objective to detect the ability of organisms to produce citrase enzyme. Principle of citrate utilization test: The basic principle of this test […]
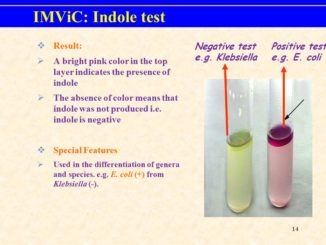
Indole test: Objective: to detect the ability of organism to produce enzyme tryptophanase. Principle: Indole test is a biochemical test which differentiates the coliform […]

Methyl red (MR) test: Objective: To check whether the organism follow mixed acid fermentation pathway during their metabolism or not Principle of MR test: The […]

Voges-Proskauer test (VP test) Objective: To check whether the microorganism follow 2,3 butanediol production pathway for glucose metabolism or not Principle of VP test: The […]

Oxidase test Objective: to check for presence of terminal enzyme Cytochrome C oxidase or Cytochrome a3. Principle of oxidase test: Oxidase is a terminal enzyme […]

Catalase test Objective: to check whether the tested microorganisms (bacteria) is aerobic or anaerobic Principle: Catalase is an enzyme that breaks Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), a […]
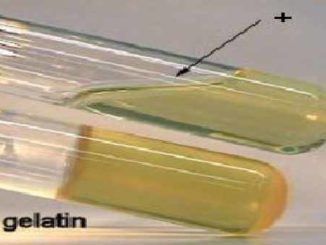
Gelatin hydrolysis test Objective: to test whether the organism produces gelatin hydrolyzing enzyme gelatinase or not Principle: The main purpose of this test is to […]
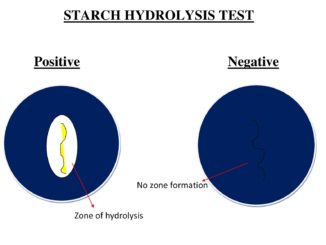
Starch hydrolysis test Objective: to test whether the organism produces the starch hydrolyzing enzyme amylase or not Introduction: The main aim of this test is […]

Acid-Fast staining (Ziehl-Neelsen technique): Principle: Acid fast staining is a differential staining technique which differentiate acid fast and non-acid fast bacteria. Mycobacterium species contains large […]
Copyright © 2024 | WordPress Theme by MH Themes