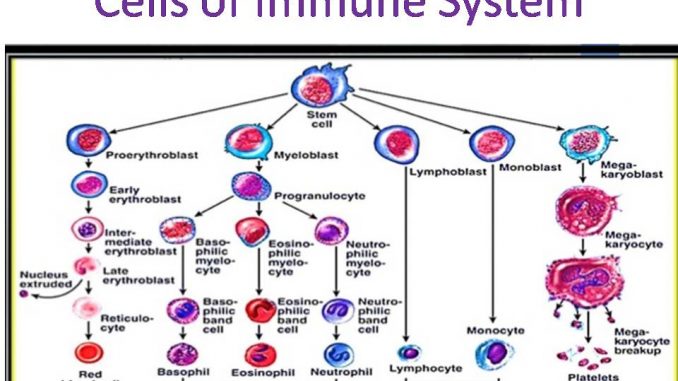
Cells of immune system: Lymphocytes, phagocytic cell, granulocytes and dendritic cells
- WBCs are the principle cells of immune system formed hematopoietic stem cell by the process of hematopoiesis. Hematopoiesis occurs in yolk sac during 1st week of gestation. After 3rd month of gestation, hematopoiesis occurs in liver and spleen of fetus and after birth, it occurs in bone marrow.
The cells of immune system are:
1. Lymphocytes-
- T-lymphocytes
- B- lymphocytes
- NK cell
2. Phagocytic cells
- Monocytes
- Macrophages
3. Granulocytic cells
- Neutrophils
- Basophils
- Eosinophils
4. Dendritic cells
I. Lymphocytes:
- Lymphocytes are small, round cells found in peripheral blood, lymph, lymph nodes, lymphoid organs and in tissues.
- Lymphocytes represent 20-45% of total cells in peripheral blood and 99% of total cells in lymph and lymph node.
- According to side lymphocytes are divided into small (5-8µm), medium (8-12µm) and large (12-15µm).
- Depending on life span lymphocytes are classified into short lived (2 weeks) and long lived (3 years or more or even lifelong).
Broadly lymphocytes are divided into three sub-populations, on the basis of function and cell membrane components.
II. Phagocytic cells:
- Monocytes and macrophages are mononuclear phagocytic cells.
- Granulocyte-monocyte progenitor cell differentiates into promonocytes and neutrophil.
- Promonocytes leaves the bone marrow and enter into blood stream where they differentiate into mature monocytes.
- Monocytes circulates in blood for about 8 hours, during which they enlarges and then enter into tissues and differentiates into specific macrophages and dendritic cells.
1. Monocytes:
- Blood monocytes measure 12-15 µm with a single lobed kidney shaped nucleus.
- It accounts for (2-8%) of blood leucocytes.
Immunological Functions of monocytes:
- Helps in antigen processing and presentation
- Releases cytokines
- Specialized function in tissues
- Cytotoxicity
2. Macrophages:
- Monocyte migrates to tissue and differentiates into macrophages.
- Differentiation of monocytes into macrophages involves following changes:
- Cell enlarges 5-10 folds
- Intracellular granules increases in number and complexity
- Increase phagocytic ability
- Produces higher level of hydrolytic enzymes and cytokines
- Macrophages serve different functions in different tissues.
- Alveolar macrophages : in lungs
- Histiocyte: connective tissue
- Kuffer cell: liver
- Messangial cell: kidney
- Microglial cell: brain
- Osteoclast: bone
Immunological functions of macrophages:
- Phagocytosis
- Antigen presentation to T-cell
- Secretion of lymphokines IL-1, IL-6. IL-12. TNF-α etc to activates inflammatory response
- Secretion of granulocyte monocyte colony (GMC) stimulating factors.
II. Granulocytic cells:
1. Neutrophil:
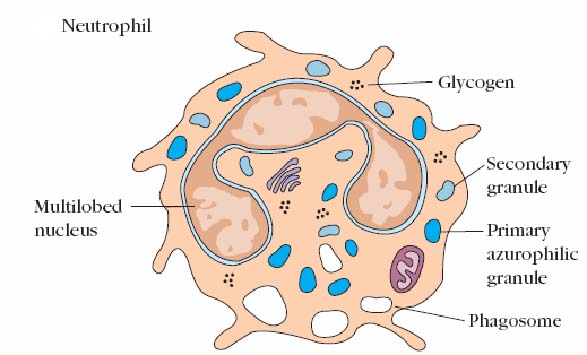
- Neutrophils are (11-14µm) in diameter with multilobed nucleus with granules in cytoplasm.
- It constitutes 50-70 % of total circulating WBC and remains for 7-8 hours in blood and then migrates to tissues
- Life span is 3-4 days.
- Also known as polymorphonuclear (PMN) leucocyte.
- Neutrophils is stained by both acidic and basic dye.
Immunological functions of Neutrophil:
- Phagocytic role in acute inflammatory response.
- It is the first immune cell to responds in inflammation.
2. Eosinophils:
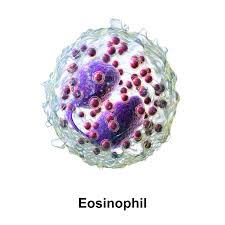
- Eosinophils are (11-15µm) in diameter, heavily granulated with bilobed nucleus
- It is stained by acidic dye ie Eosin
- They are phagocytic and motile
Immunological functions of Eosinophil:
- Granules contain various hydrolytic enzymes that kill parasites which are too large to be phagocytosed by neutrophils.
- Provide allergic inflammation
3. Basophils:
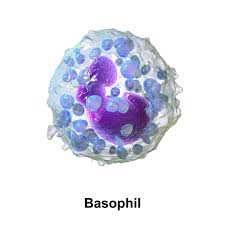
- Basophils are non-phagocytic cell found in small number in blood and tissue
- Cytoplasm contains large number of prominent basophilic granules containing histamine, heparin, serotonin, and other hydrolytic enzymes
- Stained by basic dyes
Immunological functions:
- Provide anaphylactic and atopic allergic reaction
IV. Dendritic cell:
- Dendritic cells have long cytoplasmic externsions that resembles to dendrites of nerve cell.
- They have highly pleomorphic with a small central body and many long needle like processes.
- Dendritic cells are antigen presenting cell (APC) because they possess MHC class.
Immunological functions:
- Involved in antigen presentation to T-cells during primary immune response.
- Very little role in phagocytosis.

Please write a note on molecular structure of antibodies and a note on clonal selection theory