Connective tissue: characteristics, functions and types
- Connective tissues are the major supporting tissue of the body. It is composed of variety of cells, fibre (non-living products of cell) and semi-solid matrix between cells.
Characteristics of connective tissue:
- Connective tissue ranges from avascular to highly vascular.
- Composition: Composed mainly of nonliving extracellular matrix that separates the cells of the tissue.
- Location: It is present in between different tissue and organs. It can be found in and around the body organs. skeletal tissue present in the form of bone and cartilage, and fluid connective tissue as blood and lymph are connective tissue.
Function of connective tissue:
- It binds various tissue together like skin with the muscles and muscles with bones
- It form inter cellular substance between cells of different types of tissue, so that help in friction less movement of the body organ
- It forms sheaths around the body organs and make a kind of packaging tissue
- The areolar tissue protects the body against wound and infection
- The adipose tissue stores fats and insulates the body against heat loss
- The supportive tissue forms shape and the frame work of the body
- The haemopoitic tissue produce blood
- The lymphatic tissue helps in body immunity
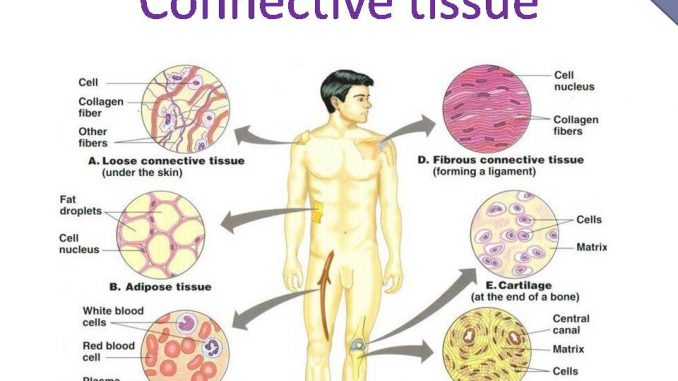
Types of connective tissue
I. Proper connective tissue: types-
- Areolar connective tissue
- Adipose connective tissue
- Reticular tissue
2. Dense (fibrous) connective tissue:
- White fibrous tissue ( tendon and sheath)
- Yellow elastic tissue (Ligament)
II. Supporting connective tissue: types-
1. Cartilage:
- Hyline cartilage
- Elastic cartilage
- Fibrous cartilage
2. Bone:
- Spongy bone
- compact bone
