
Cultivation technique of bacteria: Batch, Fed-batch and Continuous culture technique
There are three techniques for cultivation of bacteria.
- Batch culture technique
- Fed-batch culture technique
- Continuous culture technique
1. Batch culture technique
- Batch culture technique is also called as closed system of cultivation.
- In this technique at first nutrient solution is prepared and it is inoculated with inoculum (culture organism) and then nothing is added in the fermentation tank except aeration.
- In batch culture, neither fresh medium is added nor used up media is removed from the cultivation vessel. Therefore volume of culture remains same.
- Since fresh media is not added during the course of incubation, concentration of nutrition decreases continuously. Furthermore various toxic metabolites also accumulates in the culture vessel. Therefore batch culture technique gives characteristics growth curve with lag phase, log phase, stationary phase and decline phase.
Advantage:
- Chance of contamination of culture is minimum in batch culture technique because it is closed system of cultivation.
Disadvantage:
- It gives low product yield and it is not economic procedure.
2. Fed-batch culture technique:
- Fed-batch culture is also called as semi-closed system of cultivation.
- In this technique, at first nutrient media is prepared and it is inoculated with culture organism and then incubated for particulate time.
- During the course of incubation a particular nutrient is added at intervals without removing the used up media.so the volume of culture increases continuously.
- Fed batch culture technique is applied in many types of fermentation process.
- In fermentation some nutrient is very essential for the process but when these nutrients are provided in higher concentration in the culture they inhibit the growth of bacteria ultimately ceasing the fermentation. Therefore such nutrients are kept in lower concentration initially and it is added slowly and continuously during the course of fermentation.
Advantage:
- Fed batch culture gives greater product yields than batch culture technique.
Disadvantage:
- Chance of contamination of culture is higher in fed-batch than batch culture technique.
3. Continuous culture technique
- Continuous culture technique is also called as open system of cultivation.
- In this technique fresh sterile medium is added continuously in the vessel and used up media with bacterial culture is removed continuously at the same rate. So the volume and bacterial density remain same in the cultivation vessel.
- In this technique, bacteria grow continuously in their log phase. This type of growth is known as steady state growth.
- The cell density in continuous culture remains constant and it is achieved by maintaining constant dilution and flow rate.
Types of approach to continuous culture
i. Chemostat
ii. Turbidostat
i. Chemostat:
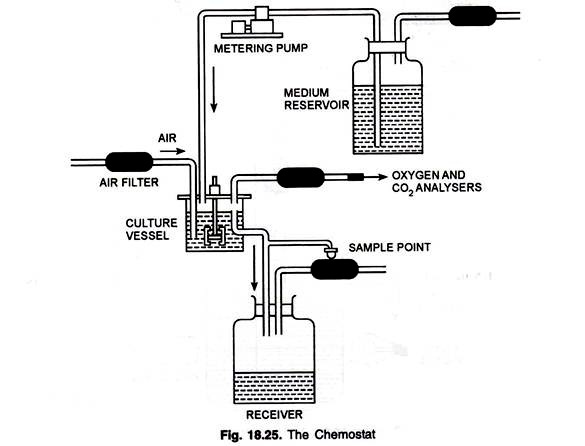
- It is the most common type of approach which controls the population density and growth of culture.
- Two elements are used in chemostat, the dilution rate and concentration of limiting nutrient.
- In continuous culture, end products do not accumulates and nutrients are not completely depleted, therefore bacteria never reach in stationary phase because fresh nutrients are supplied continuously and end products are removed continuously.
- In chemostat, the liquid media contain some nutrient in growth limiting concentration and the concentration of limiting nutrient determines the rate of bacterial growth.
- During steady state chemostat, concentration of limiting nutrient remains constant because the rate of addition of nutrient equals the rate at which it is used by organism plus flow through outlet.
- To check whether there is constant cell density or not, concentration of that essential nutrient in the vessel is checked.
- If the concentration of that nutrient is altered then it indicates bacterial density is changing. Therefore in this case flow rate is adjusted to maintain constant cell density.
ii. Turbidostat:
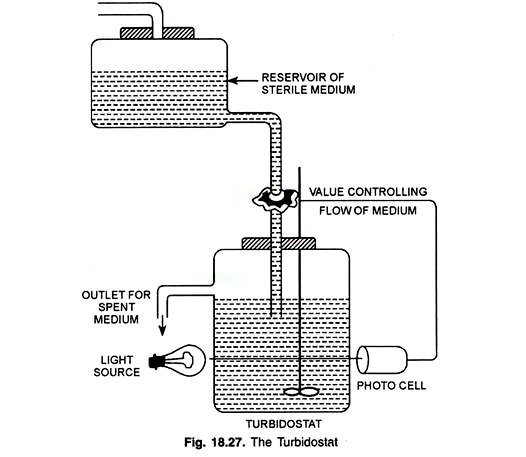
- In turbidostat, a photoelectric device is used to monitor the cell density in the cultivation vessel.
- The optical sensing device measure the turbidity (absorbance) of the culture in the vessel.
- If concentration is altered, it is noticed by the photoelectric device and the flow rate is adjusted to
- Maintain constant cell density in the culture.
