
Entner-Doudoroff (ED) pathway
- This pathway occurs in both aerobic and anaerobic condition
- Occur in prokaryotes only
- It occurs in cytoplasm
- Pyruvate and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate produced from glucose by ED pathway
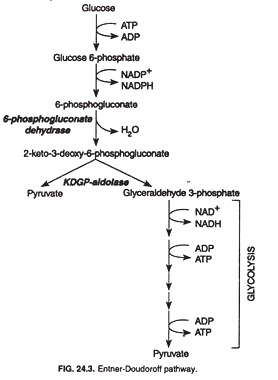
- At first glucose is phosphorylated to glucose -6-phosphate by the enzyme hexokinase.
- Glucose-6-phosphate is then oxidized to 6-phosphogluconolactone releasing a molecule of NADPH. This reaction is catalyzed by the enzyme glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase.
- Hydrolase enzyme converts 6-phopshogluconolactone to 6-phosphogluconate.
- 6-phosphogluconate undergoes dehydration reaction catalyzed by 6-phosphogluconate dehydratase to form 2-keto 3-deoxy 6-Phosphogluconate (KDPG).
- KDPG splits to form pyruvate and glceraldehyde-3-phosphate. It is catalyzed by KDPG aldolase enzyme
- Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate is then metabolized by glycolysis to form pyruvate.
Significance of ED pathway
- This pathway used two specific enzymes ie. 6-phosphogluconate dehydratase and KDPG aldolase.
- This pathway generates 1 ATP, 1 NADH and 1 NADPH from one glucose molecule.
