
Factor affecting bacterial growth
- Growth of bacteria is affected by many factors such as nutrition concentration and other environmental factors.
Some of the important factors affecting bacterial growth are:
- Nutrition concentration
- Temperature
- Gaseous concentration
- pH
- Ions and salt concentration
- Available water
1. Nutrient concentration:
- If culture media is rich in growth promoting substance, growth of bacteria occurs faster. Decrease in nutrient concentration decreases the growth rate.
- Different bacteria have different nutritional requirement.
The relationship between substrate concentration (nutrition) and growth rate is shown in figure.
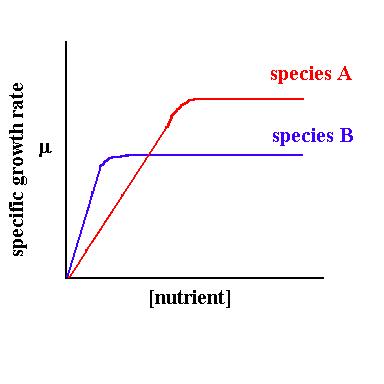 figure: nutrient vs growth rate
figure: nutrient vs growth rate
- With increase in concentration nutrition, growth rate of bacteria increases up to certain level and then growth rate remains constant irrespective of nutrition addition.
2. Temperature:
- Temperature affects the growth of bacteria by various ways.
- The lowest temperature that allows the growth is called minimum temperature and the highest temperature that allows growth is called maximum temperature.
- There is no growth below minimum and above maximum temperature.
- Below minimum temperature cell membrane solidifies and become stiff to transport nutrients in to the cell, hence no growth occurs.
- Above maximum temperature, cellular proteins and enzymes denatures, so the bacterial growth ceases.
The relationship between temperature and growth rate is shown in figure below.
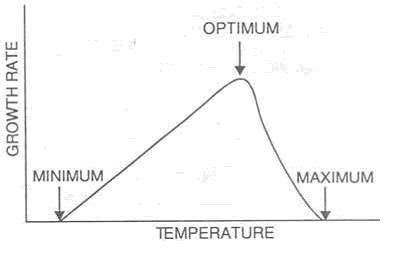
figure: temperature vs growth rate
- When temperature is increases continuously from its minimum, growth rate of bacteria increases because the rate of metabolic reaction increases with increase in temperature.
- At certain temperature the growth rate become maximum, this temperature is known as optimal temperature.
- On further increasing the temperature above optimal, growth rate decreases abruptly and completely ceases with reaching maximum temperature.
3. pH:
- pH affects the ionic properties of bacterial cell so it affects the growth of bacteria.
- Most of the bacteria grow at neutral pH (60.5-7.5). However there are certain bacteria that grow best at acidic or basic pH.
- relationship between pH and bacterial growth is given in figure below.
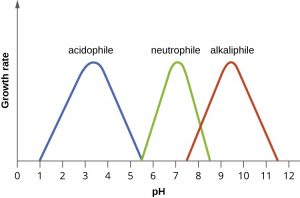
figure: pH vs growth rate
4. Ions and salt:
- All bacteria requires metal ions such as K+, Ca ++, Mg++, Fe++, Zn++, Cu++,Mn++ etc to synthesize enzymes and proteins.
- Most bacteria do not require NaCl in media however they can tolerate very low concentration of salt.
- There is some halophilic bacteria such as Archeobacteria that require high concentration of salt in media.
5. Gaseous requirement:
- Oxygen and carbon-dioxide are important gases that affects the growth of bacteria.
- Oxygen is required for aerobic respiration and obligate aerobic bacteria must require O2 for growth. Eg. Mycobacterium, Bacillus
- For obligate anaerobes Oxygen is harmful or sometime lethal. However facultative anaerobes can tolerate low concentration of O2.
- Carbon-dioxide is needed for capnophilic bacteria. Such as Campylobacter, Helicobacter pylori
6. Available water:
- Water is the most essential factor for bacterial growth.
- Available water in the culture media determines the rate of metabolic and physiological activities of bacteria.
- Sugar, salts and other substances are dissolved in water and are made available for bacteria.
