
Gene mapping
- Gene mapping is the process of determining the genes and their location along the length of chromosome.
- T. D Morgan pave the foundation of gene map by identifying gene for white eye Drosophila on X-chromosome of mutant. Later his students able to locate other X-linked gene on X-chromosome.
- The procedure of gene mapping was developed by Alfred H Sturtevent. His procedure is based on the principle of linkage. The gene located on same chromosome inherits together known as linked gene. However, some gene on same chromosome could separate during meiosis and new combination of genes are formed. The phenomenon of recombination is due to crossover and chaismata formation during meiosis.
- Gene map is by counting the number of crossovers that occur during meiosis. However, because the actual crossover events cannot be seen, they cannot count them directly. So, recombination frequency is calculated to estimate the crossover.
- Chiasmata are counted through cytological analysis, whereas recombinant chromosomes are counted through genetic analysis.
Gene map distance:
- Gene map distance is the distance between points on a chromosome which can be estimated by counting the number of crossovers between them. Therefore, the distance between two points on the genetic map of a chromosome is the average number of crossovers between them. Genetic map distances are, in fact, based on such averages.
- Points that are far apart should have more crossovers between them than points that are close together. However, the number of crossovers must be understood in a statistical sense.
- In any particular cell, the chance that a crossover will occur between two points may be low, but in a large population of cells, this crossover will probably occur several times simply because there are so many independent opportunities for it. Thus, the quantity that we really need to measure is the average number of crossovers in a particular chromosome region.
- let us consider 100 oogonia undergoes gametogenesis (meiosis).
- In some cells, no crossovers will occur between sites A and B; in others, one, two, or more crossovers will occur between these loci.
- At the end of meiosis, there will be 100 gametes, each containing a chromosome with either zero, one, two, or more crossovers between A and B.
- We estimate the genetic map distance between these loci by calculating the average number of crossovers in this sample of chromosomes.
- The result from the data is 0.42.

Two point test cross in Drosophila:
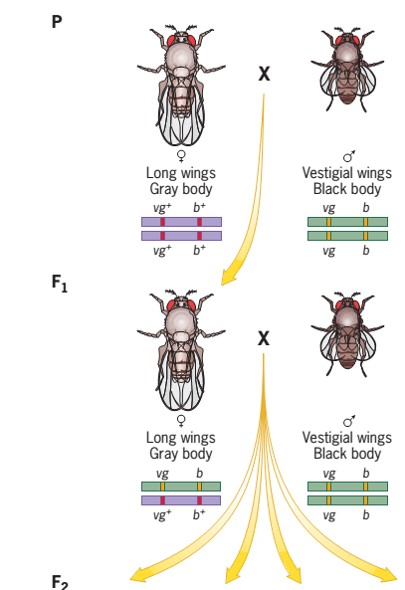
- When wild-type Drosophila Females were mated to Males homozygous for two autosomal mutations—vestigial (vg) short wings, and black (b) body coloration. Ie. Female (vg+vg+ , b+b+) and male (vg vg, b b)
- All the F1 flies had long wings and gray bodies; thus, the wild-type alleles (vg+ and b+) are dominant.
- The F1 female progeny were then testcrossed to vestigial winged black body males (vg b), and the F2 progeny were obtained and there are classified on the basis of phenotypic characters and counted.
- There were four phenotypic classes, two abundant and two rare. The abundant classes had the same phenotypes as the original parents (vestigial wing black body and long wing and grey body), and the rare classes had recombinant phenotypes (ie. vestigial wings with grey body and long wings with black body).
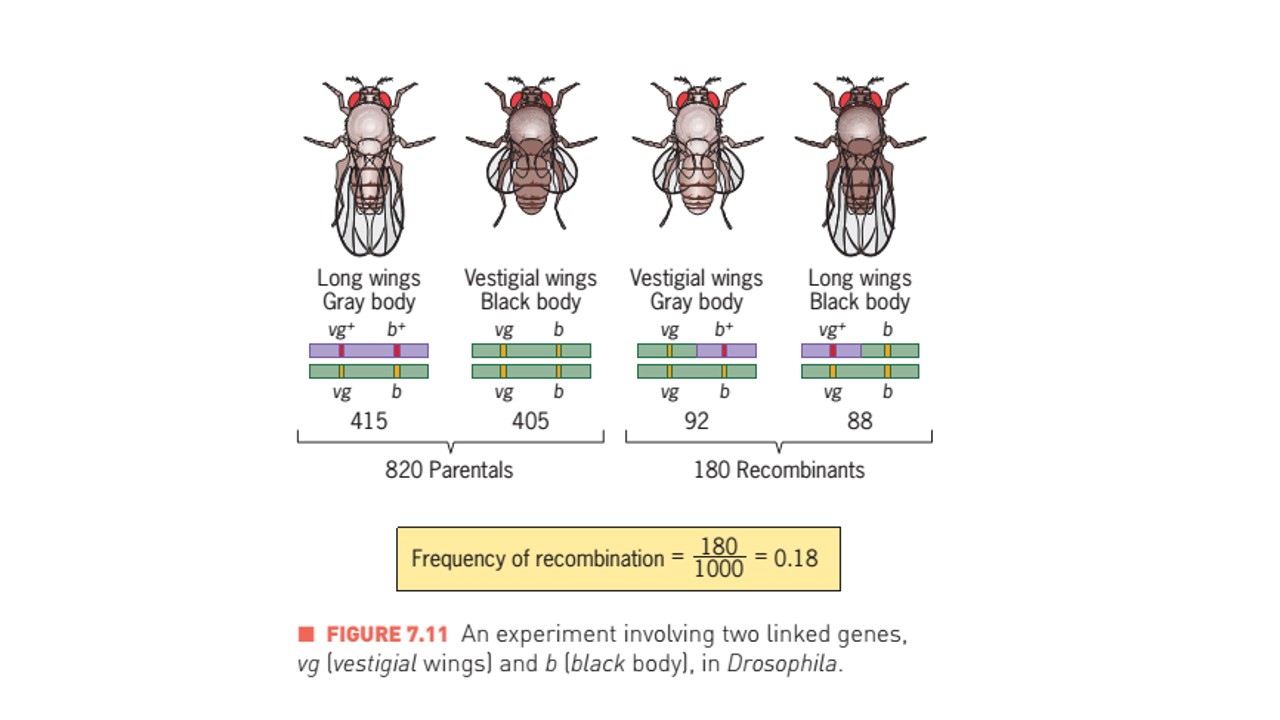
- Number of F2 Progeny with vestigial wing and black body (vg vg, b b)= 405
- Number of F2 progeny with long wing and grey body (vg+ vg+, b+ b+)= 415
- Number of f2 progeny with vestigial wing and grey body (vg vg, b+ b)= 92
- Number of F2 progeny with long wing and black body (vg+ vg, b b)=88
- The genes for vestigial wings and black body are linked because the number of recombinants are much fewer than 50 percent of the total progeny counted in F2 generation. Therefore, these genes must be on the same chromosome.
Map distance:
- Map distance is the distance between genes.
- To determine the distance between the genes for vestigial wing and black body, we must estimate the average number of crossovers in the gametes of the doubly heterozygous F1 females (vg+vg, b+b)
- Average crossover is estimated by calculating the frequency of recombinant F2 progeny
- The average number of crossovers in the whole sample of progeny is therefore,
Frequency of recombination (RF) = (0) (415+405)/1000 + 1 (92+88)/1000
=0.82+0.18
=0.18 Morgan
=18 centimorgan or map unit
- This simple analysis indicates that, on average, 18 out of 100 chromosomes recovered from meiosis had a crossover between vg and b.
- Thus, vg and b are separated by 18 units
- 100 centiMorgans equal one Morgan (M). Therefore vg and b are 18 cM (or 0.18 M) apart.
- The map distance is equal to the frequency of recombination.
