Human Heart-Gross structure and Anatomy
Heart
- Heart is a myogenic muscular organ that pumps blood throughout the blood vessel by repeated rhythemic contraction.
Figure: Anatomy of Human Heart
- Shape and size: it is roughly cone shaped hollow organ which is about 10 cm long. It is approximately the size of owner’s closed fist and weight about 250-300 gm in female and 300-350gm in male.
- Location: heart lies in the thoracic cavity in the space between the lungs (mediastinum) anterior to the vertebral column and posterior to sternum. It lies obliquely a little more to left than right.
Structure:
heart is composed of three layer of tissue.
- Pericardium
- Myocardium
- Endocardium
Pericardium
- It is double walled layer which encloses heart; the space between the two layer is filled with pericardial fluids.
- Outer layer is called fibrous pericardium
- Inner layer is called serous pericardium. It secrete serous fluid.
- During heart beat, pericardial fluid prevent heart from shock and mechanical injury
Myocardium
- Myocardium is the middle layer which is composed of specialized cardiac muscle (only found in heat)
- Myocardium is striated muscle but not under voluntary movement.
- When impulse is generated, it spread from cell to cell via branches and intercalated disc over the whole sheet of cardiac muscle causing contraction of muscle fiber.
- The sheet arrangement of cardiac muscle enables the atrium and ventricle to contract in coordinated and efficient manner.
- Myocardium is the thickest at the apex than the base. Similarly thicker at left ventricle than right ventricle. This reflects the amount of workload.
- Cardiac skeleton: The myocardium is supported by the network of fine fiber, called as fibrous skeleton of heart
Endocardium
- Endocardium is the inner layer of heart which lines the chamber and valves of the heart
- It is thin, smooth membrane that permits smooth flow of blood
- It consists of flattened epithelial cells and is continuous with endothelium layer of blood vessels.
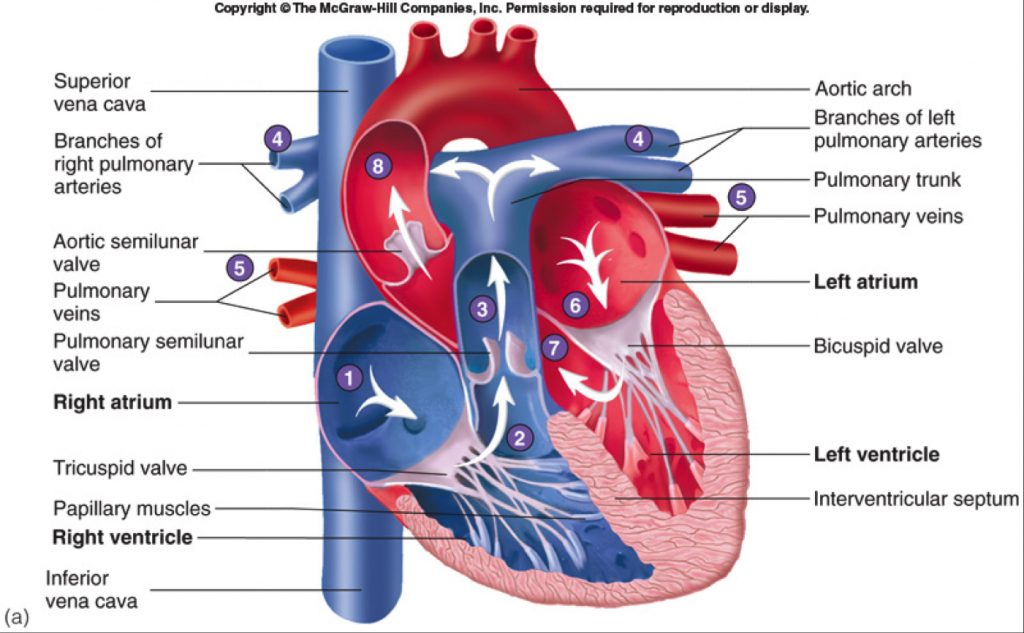
Chambers of heart:
- Heart consists of 4 chambers
- At first heart is divided into right and left side by the septum
- Each side is further divided into 2 chamber each by artioventricular valve
- The upper two chambers are called atrium and lower two are called ventricles.
Atrium
- Atrium are thin walled chamber separated by interauricular septum
- Right atrium receive impure blood from body through the opening via superior and inferior venacava
- The opening is guided by Eustachian valve and coronary valve.
- In right atrium, there is a oval depression adjoining the inter-auricular septum called fossa ovalis which communicate two auricle during fetal life
- Left atrium receive pure (oxygenated) blood from lungs through the four opening of pulmonary vein
- Each atrium has flap like appendages called auricle of unknown function
Ventricle
- Ventricles are thick walled chamber separated by thick inter-ventricular septum
- Left ventricle is thicker and longer than right ventricle
- The wall of ventricle has muscular ridges or projection called columnae cornea (Trabeculae cornae)
- Columnae cornea divides the cavity of ventricles into smaller spaces called fissures
- Right ventricle receive impure blood from right atrium and pumps via pulmonary arteries to lungs
- Left ventricle receive oxygenated blood from left atrium and pumps the blood to aorta.
Valves
1. Atrioventricular valve
- These are two in number
- The right artioventricular valve has three cusps or flaps, called tricuspid valve
- Left artioventricular valve has only two cusps, called as bicuspid valve
- These valves open only in ventricles and hence prevent back flow of blood
- These valves are attached to the wall of ventricles by means of tendon called chordae tendinae
- The function of chordae tendinae is to hold the valve and prevent enter of valve to auricle during forceful ventricular contraction.
2. Semilunar valve
- Right ventricle pumps blood through pulmonary aorta to lungs and left ventricle pumps blood through aorta. These opening is guided by three cusps semi lunar valve
- Left semilunar valve is called aortic valve and right semilunar valve is called pulmonary valve.