Principle:
- Leucine Amino Peptidase (LAP) test is one of the rapid tests which is employed for the detection of the enzyme leucine amino peptidase.
- The LAP test is generally performed for the preliminary characterization of catalase- negative, gram-positive cocci, particularly non-beta hemolytic cocci.
- Leucine-
-naphthalamide impregnated disk acts as a substrate.
- The LAP enzyme is responsible for hydrolysis of substrate that yields
-naphthalamine.
- The product on addition to p-methyl (an aminocinnamaldehyde reagent) forms a highly visible red colored Schiff’s base.
Procedure:
- Place a LAP disk in a sterile petri dish, and leave the disk to warm to room temperature.
- Lowly dampen the LAP disk either with reagent grade water or with a little sterile distilled water.
- Use a wooden applicator stick to rub a small amount of several colonies of an 18 to 24 hour pure culture onto a small area of the LAP disk.
- Incubate at room temperature for 5 minutes.
- Add 1 drop of cinnamaldehyde reagent after the incubation period, and read within one minute.
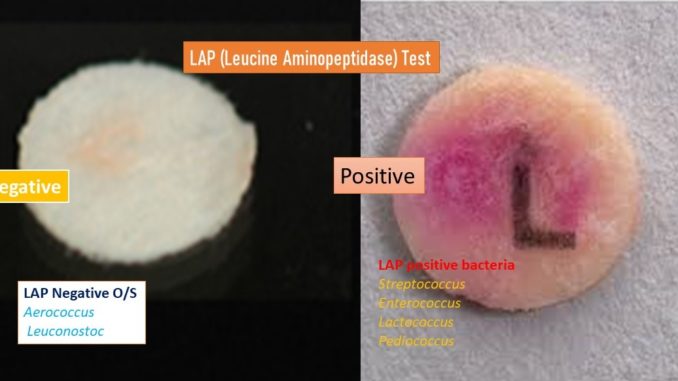
Results interpretation:
- Positive result:
- The positive test is indicated by the development of a red/pink color.
- Negative result:
- The negative test is suggested by no change or slight yellow color.
Limitations:
- The confirmation of test organism to be gram-positive coccus and catalase negative is mandatory for the LAP test.
- There might be chances of false negative if inadequate columns are taken.
