Principle:
- Microdase test is also termed as modified oxidase test.
- It is one of the rapid tests employed for the differentiation between Staphylococcus and Micrococcus which are Gram positive cocci having catalase enzyme.
- The test is based on the detection of oxidase enzyme.
- Filter paper disks impregnated with tetramethyl-p-phenylenediamine in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) is used in order to detect the oxidase enzyme.
- 1% (w/v) tetramethyl-p-phenylenediamine in certified grade dimethyl sulfoxide is the preparation for modified oxidase reagent.
- DMSO serves for the permeability of cells to the reagent along with providing solubility and stability against auto-oxidation.
- When exposed to atmospheric oxygen, the oxidase enzyme reacts with the oxidase reagent and cytochrome C to yield the coloured compound, indophenol indicated as blue or purplish blue coloration on the disc after the bacterial colony is introduced on the disc.
Requirements:
- Media: Blood agar
- Oxidase Disc
- Filter paper disks impregnated with tetramethyl-p-phenylenediamine dihydrochloride in DMSO.
- Incubator
- Forceps
- Petri dish
- Glass slide
- Fresh pure colonies of test organisms
Procedure:
- Use forceps to place the disk in an empty petri dish or on a clean glass slide.
- Use a wooden applicator stick and rub a small amount of various colonies of an 18- to 24-hour pure culture grown on blood agar onto a small area of the microdase disk.
Note: Do not rehydrate the disk before use. - Incubate at room temperature for 2 minutes.
- Observe for a blue colour development.
Results interpretations:
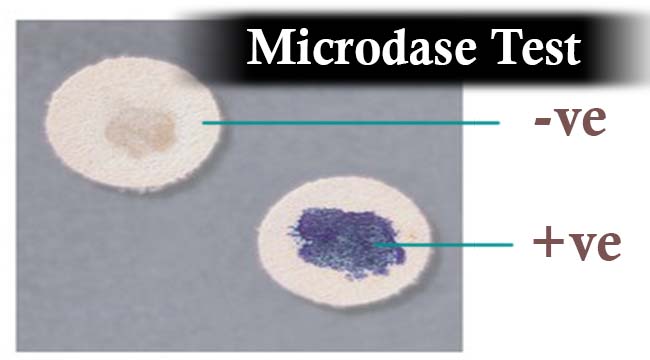
- Positive result:
- The positive test is suggested by the development of blue to purple colour within the 2 mins.
- Negative result:
- The negative test is indicated by no any change in color.
Limitations:
- Neither too young nor too old cultures are used as they might yield inaccurate results.
- Microdase test is recommended only for the Gram-positive, catalase positive cocci.
- Microdase is limited only for the routine testing of oxidase activity of Staphylococcus and Micrococcus.
