
Mold: characteristics, types of hyphae and examples
- Molds are filamentous fungi
- The body is called thallus. The thallus is made of hyphae which are cyclindrical, tube like structure that elongates by growth at tip.
- A mass of hyphae known as mycelium is responsible for filamentous nature of mold.
- The thallus of mold is made up of two part; mycelium and spore
Mycellium:
- It is the mass of hyphae
- It gives filamentous nature to mold
- Each hyphae is about 5-10um wide and composed of tube like wall surrounding the cavity, the lumen is filled or lined by protoplasm.
- Between the protoplasm and mycellial wall there is plasmacella or Cell membrane. Plasmalemma surrounds the protoplasm.
- Wall of hyphae or mycelium consists of micofibril and matrix. In most fungi microfibril is composed of chitin or hemicellulose and the matrix is made up of protein, lipid and other substances.
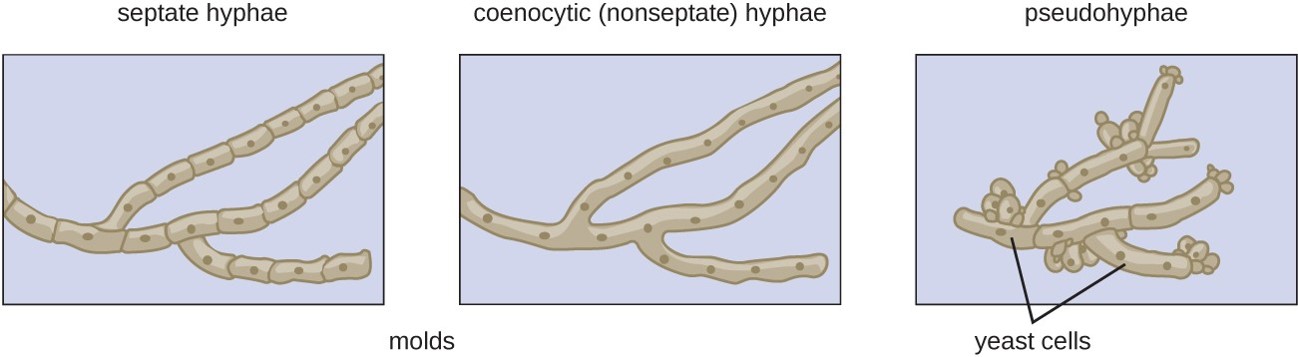
Types of hyphae:
- In some fungi hyphae is divided into cell or compartment by incomplete septum. Septum has a central pore which allows the movement of cytoplasm from one cell or compartment to another.
- There are three types of hyphae among fungi.
- Coenocytic or non-septated hyphae
- Septate hyphae with uninucleated cell
- Septate hyphae with multinucleated cell
- Hyphae can be vegetative or reproductive
- Vegetative hyphae: It penetrates the soil or medium to absorb nutrition and moisture
- Reproductive hyphae: These are aerial hyphae and form spores for reproduction.
- Examples of some mold:
- Rhizopus
- Mucor
- Absidia
- Basidiobolus
- Trichophyton
- Epidermophyton
- Histoplasma capsulatum
- Penicillium
- Aspergillus
