Monoclonal antibodies (Mabs)
- Antibodies are glycoprotein synthesized in blood against specific antigens hust to combat and give immunity. Such antibodies are heterogenous and are polyclonal antibodies. Therefore they do not have characteristics of specificity.
- If a specific lymphocyte after isolation and culture invitro becomes capable of producing a single type of antibody which bears specificity against specific antigen, it is known as monoclonal antibody.
- These monoclonal antibodies are derived from a single clone of cell which recognize only one kind of antigen.
- Monoclonal antibodies are produced against a variety of proteins, glycoproteins, glycolipids, nucleic acids and chemically defined groups linked to protein carriers.
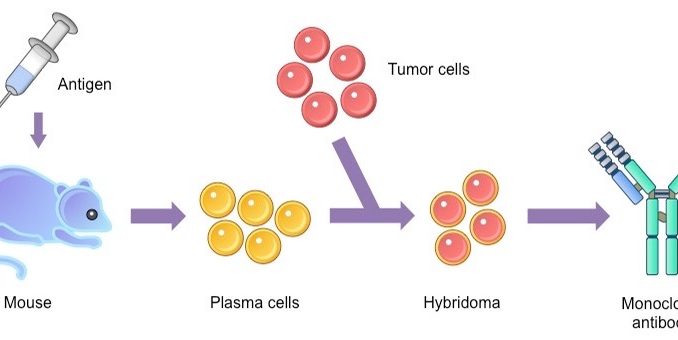
Hybridoma technology for production of monoclonal antibodies:
- Monoclonal antibodies are produced by hybridoma technology.
- The term hybridoma is used to fused cells
resulting due to fusion of following two types of cells-a lymphocytes and tumor
cell.
- An antibody producing B- lymphocytes ( eg. Spleen cell of mouse immunized with RBCs from sheep)
- A single myeloma cell (eg. Bone marrow tumor cell) that can adopted to grow for infinite time in culture
- The fused product derived the ability of two different types of cells. ie. Ability to produce large amount of pure antibodies as lymphocytes and ability to grow or multiply indefinitely like tumor cell.
Steps in production of monoclonal antibodies:
Step I: Immunization of rabbit or rat and extraction of B-lymphocytes
- In order to isolate B-lymphocyte producing certain antibodies, rabbit or lab rat is immunized through repeated injection of specific antigen (sheep RBCs)
- A sample of B-cells is extracted from spleen of rabbit or rat
Step II: fusion of myeloma cell with B-lymphocytes:
- The extracted B-lymphocytes is added to a culture of myeloma cell from bone marrow.
- The intended result is the formation of hybridoma cells formed by fusion of B-cell and myeloma cell.
- The fusion is done by using Polyethylene glycol (PEG) or by electrophoration or by using phages.
Step III: selection of hybridoma cell
- The next step is selection of hybridoma cells.
- The B-lymphocytes contains HPRT1 gene which codes for enzyme Hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase (HGPRT). The enzyme HGPRT involved in synthesis of nucleotides from Hypoxanthine present in culture medium. Therefore B- cells can grow in medium containing Hypoxanthine amonopterin thymine (HAT media).
- But myeloma cell lack HPRT1 gene so, it does not produce HGPTR enzyme and it does not grow in HAT medium.
- The myeloma cell fused with another myeloma cell or those do not fused at all die in HAT medium since they do not utilize Hypoxanthine.
- Similarly, B- cell that fuse with another B- cell or those do not fuse at all die eventually because they do not have capacity to divide indefinitely,
- So, only hybridoma cell ie. fused cell between myeloma and B-cell can survive and divide in HAT medium.
- Screening is done to select hybridoma cells which are the desired cell for monoclonal antibodies production.
Step IV: culture of Hybridoma cell:
- The selected hybridoma cells are cultured in suitable culture medium, often supplemented with insulin, transferon, ethanol, amine and other additional hormones.
- Some commonly
used culture media for hybridoma cell for production of monoclonal
antibodies are:
- DMEM (Dulbecco’s modified eagle medium)
- IMDM (Iscove’s Modified Dulbecco’s Medium)
- Ham’s F12
- RPMI 1640 medium (Roswell Park Memorial Institute 1640 medium)
Step V: Inoculation of hybridoma cell into suitable host
- These hybridoma cells are then injected into lab animal so that they starts to produce monoclonal antibodies.
- These hybridoma cells may be frozen and store for future use.
Step VI: extraction and purification of Monoclonal antibodies:
- Monoclonal antibodies from host animal is extracted and purified by one of the following methods;
- Ion exchange chromatography
- Antigen affinity chromatography
- Radial immunoassay
- Immune precipitation
Application of Monoclonal antibodies:
- Disease diagnosis:
- ELISA to test HIV, hepatitis, Herpes etc
- RIA- to test viral infection
- Mabs to Hunam chorionic gonadotropin
2. Disease treatment
- OKT3- it is an antibody to T3 antigen of T cell which can be used to prevent acute renal allograph rejection in human.
- Different types of Mabs are used in radial immunodetection and radial immune therapy of cancer.
3. Passive immunization or disease prevention
- Monoclonal antibodies based drugs can be used to treat septic shock
- Used as vaccine
4. Detection and purification of biomolecules
- Mabs are very useful in determining the presence and absence of specific proteins through western blotting technique.
- Besides that, it can be used to classify strains of a single pathogen. Eg. Neisseria gonorrhea can be typed using Monoclonal antibodies.
List of Types of monoclonal antibodies approved for therapeutic application
- Abciximab
- Trade name: Reopro
- Used after angioplasty to prevent blood clot in coronary artery
- Adalimumab
- Trade name: Humira, Amjevita
- Used to treat rheumatoid arthritis
- Alefacept
- Trade name: Amevive
- Used as immunosuppressive drug
- Alemtuzumab
- Trade name: Campath
- Used for the treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia, cutaneous T-cell lymphoma and T-cell lymphoma
- Basiliximab
- Trade name: Simulect
- Used as immunosuppressive drug
- Belimumab
- Trade name: Benlysta
- Used as immunosuppressive. It inhibits B cell activation.
- Bezlotoxumab
- Trade name: Zinplava
- Used to treatment of recurrence of Clostridium difficile infections
- Canakinumab
- Trade name: (Ilaris
- Used to neutralize Interlukin I beta
- Certolizumab pegol
- Trade name: Cimzia
- Used for the treatment of Crohn’s disease, rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis
- Cetuximab
- Trade name: Erbitux)
- Used for the treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer, metastatic non-small cell lung cancer and head and neck cancer.
- Daclizumab
- Trade name: Zenapax, Zinbryta
- Used for the treatment of adults with relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis
- Denosumab
- Trade name: Prolia, Xgeva
- Used for the treatment of osteoporosis, treatment-induced bone loss, metastases to bone, and giant cell tumor of bone.
- Efalizumab
- Trade name: Raptiva
- Used for treatment of autoimmune disease
- Golimumab
- Trade name: Simponi, Simponi Aria
- Used to treat rheumatoid arthritis
- Inflectra
- Trade name: Remicade
- Used to treat rheumatoid arthritis
- Ipilimumab
- Trade name: Yervoy
- Used to activate immune system
- Ixekizumab
- Trade name; Taltz
- Used to treat autoimmune disease
- Natalizumab
- Trade name: Tysabri
- Used for the treatment of multiple sclerosis and Crohn’s disease.
- Nivolumab
- Trade name: Opdivo)
- Used to treat cancer
- Olaratumab
- Trade name: Lartruvo
- Used to treat tumor
- Omalizumab
- Trade name: Xolair)
- Used in treatment of allergies
- Palivizumab
- Trade name: Synagis)
- Used for treatment of Respiratory syncytial virus
- Panitumumab
- Trade name: Vectibix
- Used for colorectal cancer
- Pembrolizumab
- Trade name: Keytruda
- Used in cancer immunotherapy
- Rituximab
- Trade name: Rituxan
- Used to treat autoimmune disease
- Tocilizumab
- Trade name: Actemra
- Used as Immunosupressive drugs
- Trastuzumab
- Trade name: Herceptin
- Used in treatment of breast cancer
- Secukinumab
- Trade name: Cosentyx
- Used for treatment of psoriasis, ankylosing spondylitis, and psoriatic arthritis.
- Ustekinumab
- Trade name: Stelara
- Used for treatment of Psoriasis and Crohn’s disease
