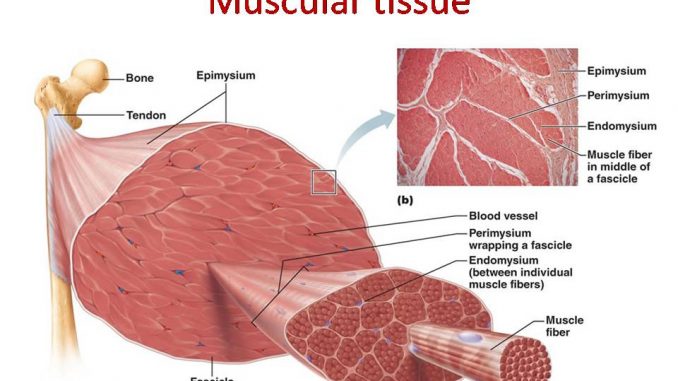
Muscular tissue: skeletal, smooth and cardiac muscle
- Muscles are made up of highly specialized thin and elongated cells called muscle fibres. The muscle fibres contains specialized cytoplasm called sarcoplasm that contain network of the membrane called sarcoplasmic reticulum. The muscle fibres may be bounded by the cell membrane called sarcolemma. Each muscle fibre may contain numerous longitudinal fibrils called myofibrils.
Basic physiological property of muscle tissue
- Contractibility
- Excitability
- Extensibility
- Elasticity
Types of muscle
- skeletal muscle
- smooth muscle
- cardiac muscle
1. Skeletal muscle:
- It acquires its name because most of the muscles involved are attached to skeleton, and make it move.
- Also known as Striated muscle -because it cell (fibre) are composed of alternating light and dark band (stripe).
- Also known as voluntary muscle
Structure-
- Composed of muscle fibres. Each muscle fibre is long, cylindrical shaped with numerous nuclei.
- Each fibre is 1.2 inch long and 0.004 inch in diameter ( longest fibre-Sartorius muscle;12 inch, shortest fibre- stapedius muscle;0.04 inch)
- Each fibre contains numerious myofibrils, which are made up of thick and thin threads called
- Thick myofilament is composed of larger protein-
- Thin myofilament is composed of smaller protein- actin
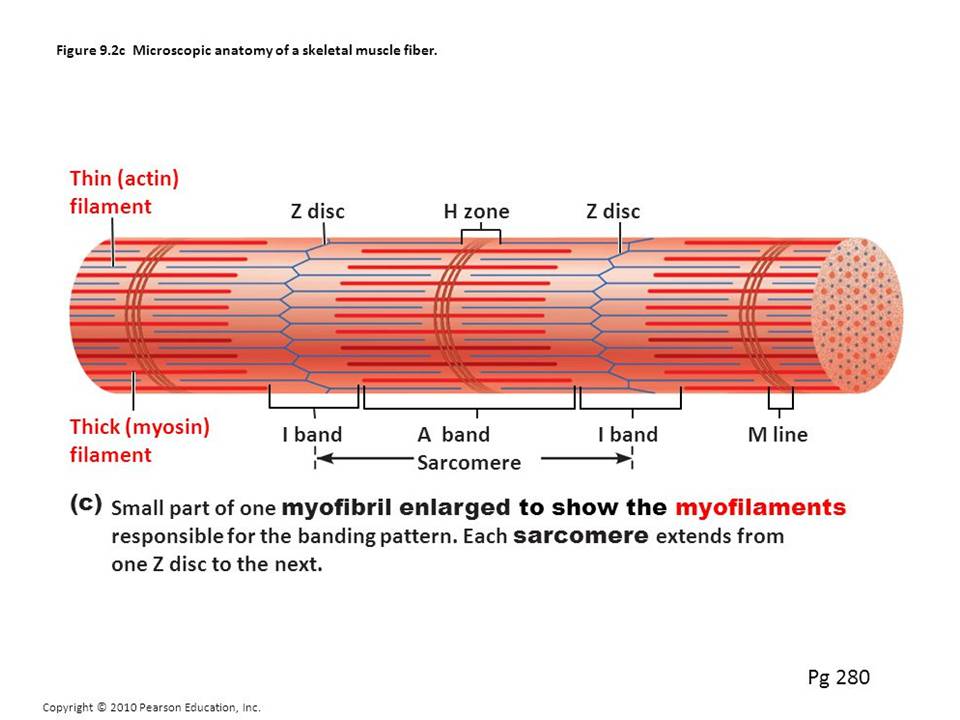
- When viewed with light microscope, skeletal tissue shows a pattern of alternating light and dark bands. The bands are caused by th earrangement of actin and myosin myofilament in the muscle fibre.
- An overlapping of thick myosin and actin myofilaments produce- dark A band (anisotropic band);doesnot allow light to pass
- Thin actin myofilament alone produce- light I band(isotropic band);allow light to pass.
- Cutting across each I band is a dark Z line
- Within A band is a somewhat light H zone( Hensen’s disc), which consists only myosin myofilament
- The area between two Z line is known as sarcomere, which is the fundamental contractile unit of myofibril
Functions: Voluntary in functions. They bring about the movement of the organs and locomotion of the body
- Skeletal muscles undergo powerful and rapid contractions with short rest periods and hence get fatigued easily.
- They are supplied by voluntary Nervous system (CNS and PNS).
- They require large amount of energy, so are supplied with blood vesssels and numerous elongated mitochondria and glycogen granules.
- Found- attached to head, trunk, limbs, also in body wall, tongue, pharynx, oesophagus
2. Smooth muscle:
- It get its name because it is not striated, and appear smooth under microscope.
- Also called involuntary muscle because it is controlled by ANS
Structure
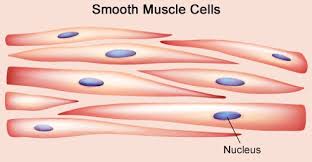
- Muscle fibre is long (but not nearly as long as skeletal muscle fibre),spindle shaped and slender. Contain only one nucleus, situated at the centre of the fibre at the broadest part
- Smooth muscle fibre is enclosed by sarcolemma, and contain numerous longitudinal myofibrils
- Actin and myosin myofilaments within myofibrils are very thin and are arranged more randomly than in skeletal muscle, so there is no stripes.
- 2 main characterstics
- Its contraction and relaxation period are slower
- Its action is rhythemical. Its contraction may last for 3o sec or more, but it doesnot tired easily. Such sustained contraction puls the ability to stretch made it suitable to muscular control of stomach, intestine, urinary bladder, uterus
3. Cardiac muscle:
- It is present only in heart
Structure-
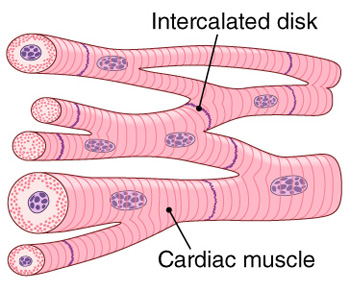
- Under microscope, they have similar striation as skeletal muscle
- Cardiac muscle cells are closely packed but each cell are nucleated and separated from each other
- The cells are joined end to end by the specialised cell junctions called intercalated disks that attach one cell to another with desmosomes, connect the myofibril filaments of adjacent cells and contain gap junctions that help to syncronise the contraction of cardiac muscle, by allowing impulse transmission from one cell to another.
- They contain light I and dark A band, the intercalated disk always occur at the location of Z-line
- Supplied with central and autonomous nervous system
- The rhythmic contraction on its own
- They don’t get fatigue, so called as fatigue less muscle.
