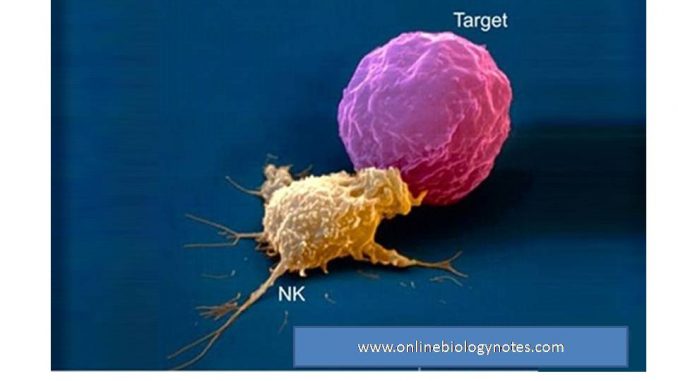
Natural killer (NK) cell
- Natural Killer (NK) cells are large granular lymphocytes (LGL) present in small proportion in spleen and peripheral blood.
- Unlike T-cell and B-cell, NK cell lacks specific antigen receptor.
- They are called as natural killer cell because they do not require activation in order to kill tumor cells or virus infected cells.
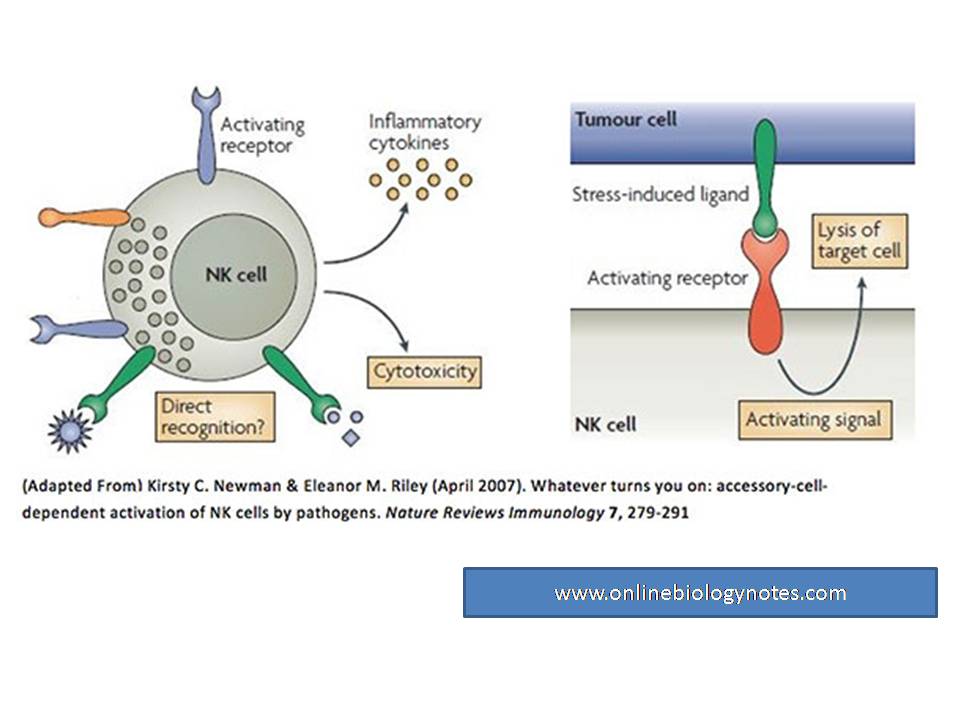
Although NK cells have no TCR or immunoglobulin in their cell membrane, they can recognize potential target cell by two ways:
i. NK cell receptor mediated:
- NK cell employs NK cell receptors to distinguished abnormal host cell, notably a reduction in display of class-I MHC molecule and unusual profile of surface antigen displayed by some tumor cell and virus infected cells.
ii. ADCC (antibody dependent cell mediated cytotoxicity):
- NK cell recognize target cell because tumor cell or virus infected cell express some antigen on their surface which is recognized by specific antibody.
- It also express CD16 which recognize Fc region of IgG antibody. they attach to these antibody and subsequently destroy the target cells.
Immunological functions of NK cells:
- Provide antitumor immunity
- Provide antiviral immunity
- provide antibody dependent cell mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC).
- secretes cytokines
