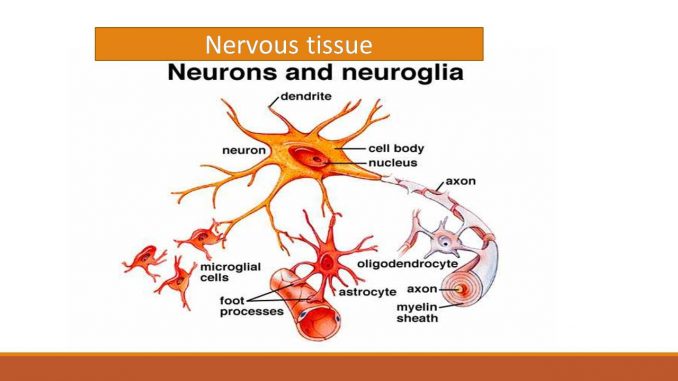
Nervous tissue: Neuron and Neuroglia
- Nervous tissue contains densely packed nerve cell ( neuron),which are specialized for nerve impulse conduction.
- Origin- ectoderm
- Nervous tissue consists of
- Neuron or nerve cell (functional unit of Nervous system)
- Neuroglia (glial cell)
Neuron:
- About 100 billions of neurons are present in nervous system.
- They are Specialised type of cell, they vary in shape and size, all neurons contains three principle parts- cell body, dendrites and an axon
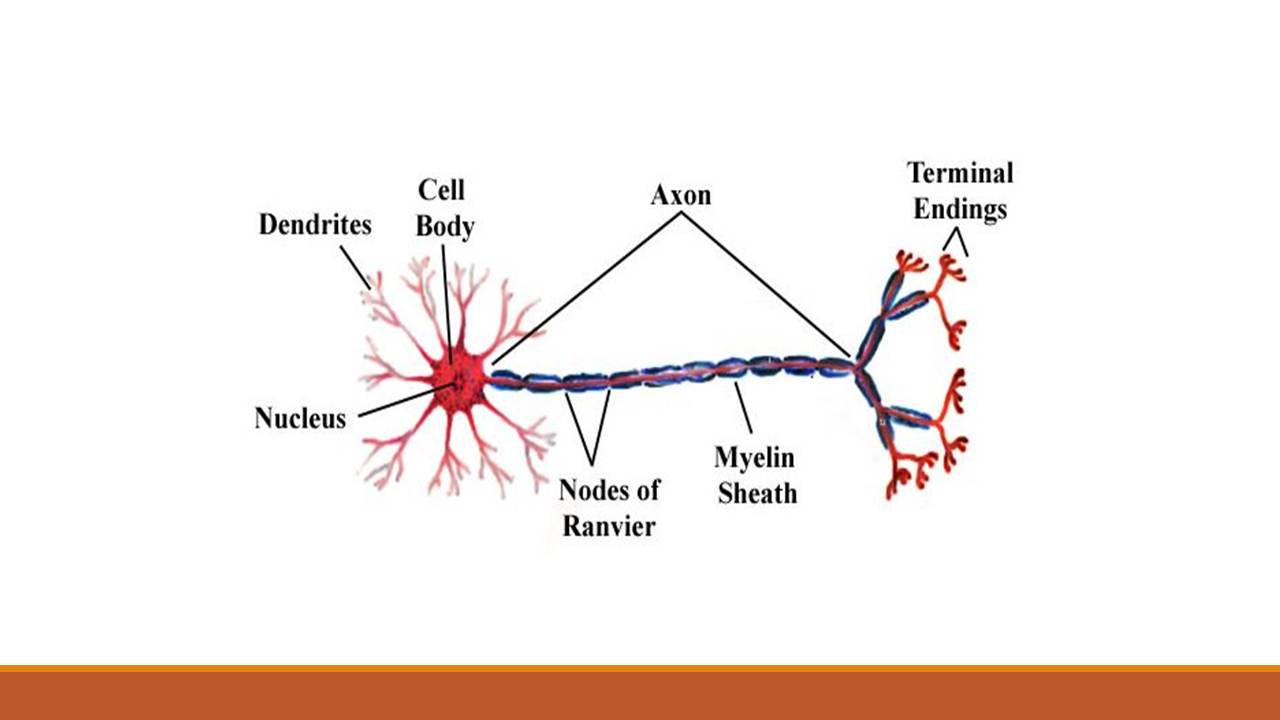
Cell body
- Has a large nucleus, which contain prominent nucleolus, as well as other several structures (Nissl bodies, ER,lysosome, mitochondria, neuroflament), responsible for metabolism, growth and repair of neuron
- Nissl bodies- made up of RNA, RER and free ribosome, help in protein synthesis
- Neurofilament and neurotubules are thread like protein, runs parallel to long process
- Neurofilament- semisolid structure that provide skeletal framework to axon
- Neurotubules- transport intracellular proteins between cell body and the processes
Dendrites-
- Many thread cytoplasmic extension arises from cell body called dendrites
- It conducts nerve impulse toward the cell body
- They are myelinated and have Nissl’s granule and neurofibril
Axon-
- Usually one of the cytoplasmic extension is long and unbranched called axon.
- It is covered by lipid sheath called myelin sheath
- Myelin sheath is formed by specialized non-neural cell called schwann cell (neurolemmocytes) in PNS and by Oligodendrocytes in CNS. The outer sheath of these cell is known as neurolemma
- It conduct nerve impulse away from cell body
- It lacks nissl’s granules
Types of neuron:
I. Types of neuron based on structure-
- Unipolar- have single processes, very common sensory neuron in PNS,
- Bipolar- two processes- a dendrires and an axon, eg. Retina, cochlea, smell receptor
- Multi polar-many processes- many dendrites but one axon eg. Brain and spinal cord
II. Types of neuron based on function-
- General somatic afferent (sensory)- carry sensory impulse from skin, skeletal muscles, joints and connective tissue to CNS
- General visceral afferent- impulse from visceral organ to CNS
- General somatic efferent(motor)- CNS to skeletal muscles
- General visceral efferent- CNS to visceral organs
- Special visceral efferent- brain to muscles of jaws, pharynx, facial expression, larynx
- Special afferent- receptor cell (olfactory, optics, auditory, vestibule, gustation) to CNS
2. Neuroglia
- Glial cells are non conducting cells that protect and nurture as well as support cells of nervous tissue.
- There are 4 types of neuroglia cells
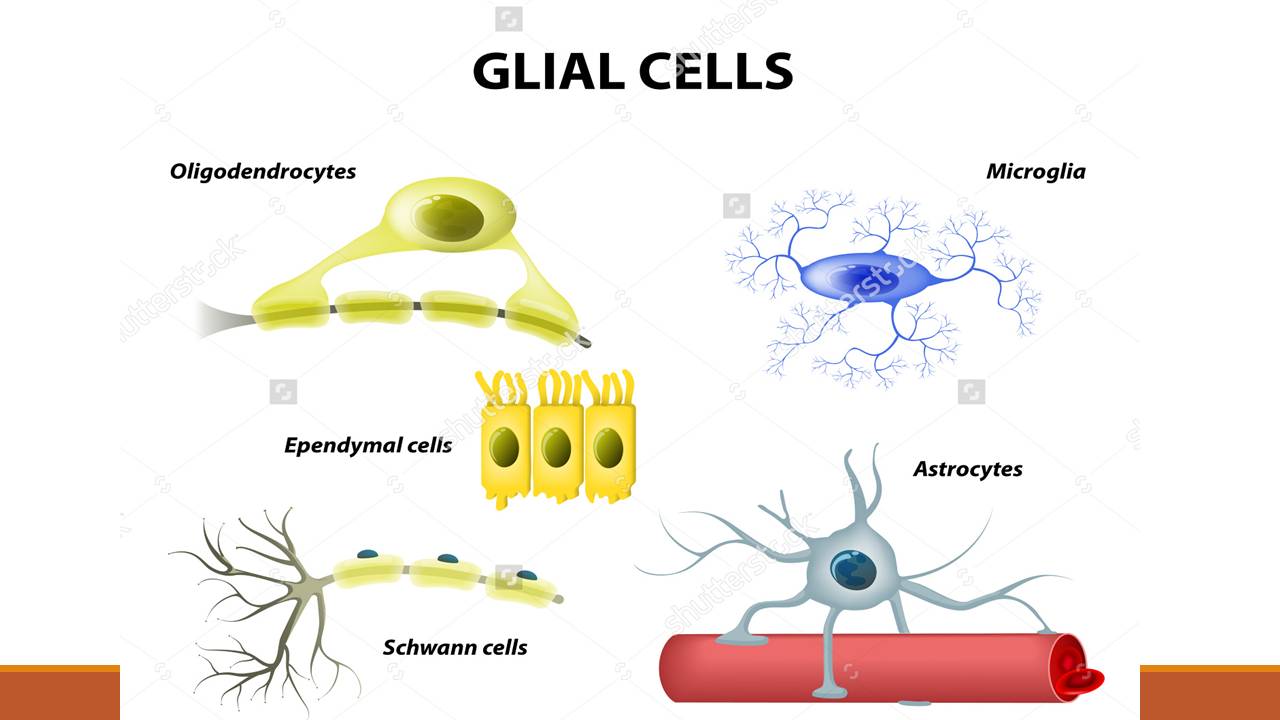
i) Astrocytes–
- largest,most numerous glial cell, with long star like processes, help form the blood –brain barrier.
- Function: structural support, transport of substance between blood vessels and neurons, mop up excess ions (k) and neurotransmitters.
ii) Oligodendrocytes-
- relatively small, with several branching processes,found in grey and white matter of CNS,
- function: produce myelin sheath
iii) Microglial cell–
- smallest glial cell, cuboidal or columnar shaped, it is a macrophage, engulf damaged neuron
iv) Ependymal cell-
- elongated cell, arranged in single layer in inner lining of spinal cord and ventricle of brain.
