
Agglutination test, types and examples
Agglutination test: Agglutination test use visible clumping of cell or cellular antigen by binding of antibody. The resulting clump or aggregate of cell is called […]

Agglutination test: Agglutination test use visible clumping of cell or cellular antigen by binding of antibody. The resulting clump or aggregate of cell is called […]

Precipitation test When bivalent antibody combines with multivalent soluble antigen, visible precipitation is formed which is indicator of antigen-antibody reaction. If precipitate remains suspending instead […]

Principle: Cetrimide is a quaternary ammonium, cationic detergent that is toxic to most bacteria, except Pseudomonas aeruginosa and a few other bacteria. Nitrogen and phosphorus […]
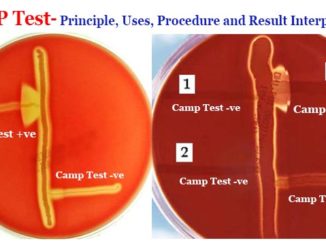
Principle: This test was first described by Christie, Atkins and Munch-Petersen (1944) and the test name CAMP is derived from the initials of the author’s name. […]
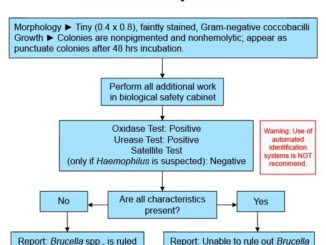
Brucella spp Brucella is a fastidious, aerobic, small, gram-negative coccobacillus that is slow growing and difficult to isolate. Four species of Brucella are recognized causing […]
Principle: Acridine orange is a fluorochromatic dye which binds to nucleic acids of bacteria and other cells that causes deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) to fluoresce green […]
Principle A capsule is non-ionic and very delicate structure that is secreted by the cell and that surrounds and adheres to the cell wall. It […]

There are many different types of transposons in eukaryotes which vary in size, structure, composition and behavior. All the eukaryotic transposons have basic characteristics such […]

There are two main type of transposable elements in bacteria having different size and structure. They are; Insertion sequences (IS elements) Prokaryotic Transposons (Tn): Composite […]
Transposable elements are the specific sequence of DNA which is mobile in nature and have capacity to transport from one position to another position in […]
Copyright © 2024 | WordPress Theme by MH Themes