
Penicillin production commercially by fermentation biotechnology
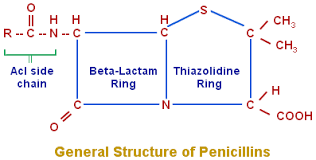
Structure of Penicillin:
- The basic structure of penicillin consists of a thiozolidine ring condensed with a B-lactum ring.
- Natural penicillin is 6-amino-penicillinic acid (6APA).
Fermentation biotechnology for penicillin production:
- By fermentation technology penicillin is produced from Penicillium spp. If penicillin fermentation is carried out without addition of side chain precursor, the natural penicillins are produced. But fermentation can be better controlled by adding a side chain precursor to obtain derived penicillin. The synthetic penicillins are produced by enzymatic hydrolysis of 6APA by penicillin acylase enzyme and then addition of desired side chain by chemical means,
- B-lactum thiozolidine ring of penicillin is constructed from l-cystine and l-valine. These two amino acids when combined with L-α-aminoadipic acid (α-AAA) the tripeptide is formed which undergoes two step cyclization process to give isopenicillin.
Regulation of penicillin production:
- The amino acids lysine is synthesized from a pathway that involves L-α-AAA, so that penicillin and lysine share a common but branched biosynthetic pathway. Higher concentration of lysine causes feed back inhibition of homocitrate synthase, an enzyme involved in α-AAA synthesis. Either lysine level should keep low or α-AAA level should added during fermentation.
- Penicillin biosynthesis is affected by Po4—concentration and also shows a distinct catabolic repression by glucose. Therefore, either slowly metabolizable sugars such as lactose is used or fed continuously with glucose with small dose.
Penicillin Production process:
- Penicillin production is previously achieved by surface process ie. Solid state fermentation and surface liquid ferementation. Now a days acommercial production is carried out by fed batch process
-
Inoculum (Organism): Penicillium chrysogenum (improved strain)
i. Inoculum preparation:
- For inoculum preparation, spore from heavily sporulated working stocks are suspended inwater or non-toxic wetting agensts (sodium sulfonate 1: 10000)
- Theses spore are then added to flask containing wheat bran and nutrient solution for heavy sporulation
- Incubate for 5-7 days at 24C
- Spore are then transferred to seed tank and incubated for 24-48 hours at 24C with aeration and agitation for sufficient mycelial growth
- These mycelia can be used for production fermenter
ii. Production fermentation:
- Method: fed-batch or batch
- Substrate: glucose, phenoxyacetic acid (fed component used for production of side chain), Corn steep liquor, Additional nitrogen source ie, soyameal, yeast extract, Lactic acid, inorganic ions, growth factors
- Fermenter: stirred tank or air lift tank
- pH: set at 5.5 t0 6.0 which increased upto 7-7.5 (optimum) due to liberation of NH3 gas and consumptionof lactic acid. If pH is 8 or more, CaCO3 or MgCO3 or phosphate buffer is added
- temperature: 25-27 C
- aeration: 0.5-1 vvm (initially more, latter less O2 )
- agitation: 120-150 rpm)
- time: 3-5 days
- antiform: edible oil (0.25%)
iii. Product recovery:
- harvest broth from fermenter tank by filtration (rotary vaccum filtration)
- chill to 5-10 C (because penicillin is highly reactive and destroyed by alkali and enzyme)
- acidify filtrate to pH 2.0-2.5 with H2SO4 ( to convert penicillin to its anionic form)
- extract penicillin from aqueous filtrate into butyl acetate or amyl acetate (at this very low pH as soon as possible in centrifugal counter current extractor)
- discard aqueous fraction
- allow the organic solvent to pass through charcoal to remove impurities and extract penicillin from butylacetate to 2% aqueous phosphate buffer at pH 7.5
- acidify the aq. Fraction to pH 2-2.5 with mineral acid and re-extract penicillin into fresh butylacetate ( it concentrated upto 80-100 times)
- add potassium acetate to the solvent extract in a crystallization tank to crystalize as potassium salt
- recover crystal in filter centrifuge
- sterilization
- further processing
- packaging
Application of penicillin:
- clinical uses of penicillin:
- naturally effective antibiotics against gram + bacteria
- used for treatment of bacterial endocarditis
