Peptide: Types and functions
- Peptide (peptide bond) is amide linkage formed by the reaction between α-carboxyl group of one amino acid and α-amino group of another amino acid with the elimination of water molecule.
- Peptide bond has partial double bond character so it is shorter than single bond and longer than double bond.
- Peptide bond is rigid and planner.
- The partial double bond character of peptide bond, prevent free rotation of polypeptide chain.
- The peptide bond is ‘trans’ It never occurs in ‘cis’ configuration due to steric hindrance.
- -COO and -NH group of peptide bond does not ionize but is polar, so it can form hydrogen bond during formation of secondary structure of proteins.
Types of peptides
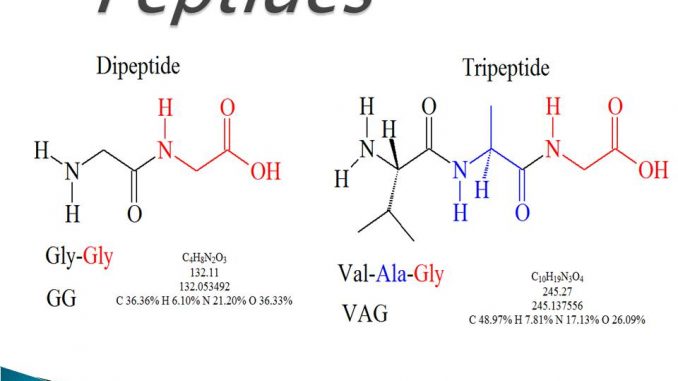
1. Dipeptides:
- Compound formed when two amino acids linked by 1 peptide bond.
- Examples:
- Carnosine ( β-alanyl-L-histidine)
- Anserine (β-alanyl-N-methylhistidine)
- Aspartame (Asparagine-phenylalanine)
2. Tripeptides
- Compound formed when three amino acids linked by 2 peptide bond.
- Examples;
- Glutathione ( Glutamyl-cystinyl-glycine)
- Opthalmic acid (L-γ-Glutamyl-α-L-amino butyrl-glycine)
3. Oligopeptides
- Compound formed when more than 2 and less than 20 amino acids are linked by peptide bonds.
- Examples;
- Tetrapeptide; Tulfsin ( thrionine-lysine-proline-Arginine)
- Endomorphin-1 ( Tyrosine-proline-tryptophan-phenylalanine)
- Amanitin ( Decapeptide)
- Netropsin
4. Polypeptides
- what is a polypeptide?
- Compound formed when more than 20 amino acids are linked by peptide bond.
- Examples:
- Insulin
- Growth hormone
Functions of peptides:
- i. Precursor of protein: Peptides are precursor of protein.
- ii. As alkaloids: Peptides are also the constituents of alkaloids (Alkaloids are group of secondary metabolites such as Nicotin, Caffeine, Terpentine, Ergotamine etc).
- iii. As Antimicrobial agent: Peptides possess antibacterial properties. Secondary metabolites of bacteria and fungi have antimicrobial activity. Eg. Penicillin G ( valine-cystein-phenylacetic acid)
- iv. As Hormones: Peptides acts as hormones eg. Insulin, Somatostatin, vasopressin etc
- v. Peptides also acts as growth factors. Eg. Ascorbic acid (vit. C)
- vi. As anti-oxidant: Peptide functions as anti-oxidant. They scavenge free radicals. Eg. Carnosine
- vii. Clinical diagnosis: hyper secretion of peptide in urine is indicator for mental state of disturbance like depression, schizophrenia etc.
- viii. As structural component: peptides form long chains creating structural protein which provides support to body. Eg. Keratin, collagen
