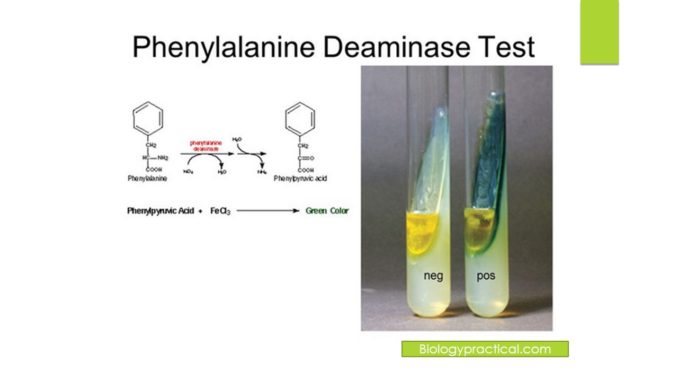
Principle:
- The phenylalanine deaminase (PDA) test is employed to differentiate among the urea- positive gram-negative bacilli on the basis of the ability of the microorganisms to produce phenyl-pyruvic acid by oxidative deamination. This test is also known as phenyl-pyruvic acid (PPA) test as Phenylalanine is an amino acid that, upon deamination by oxidase enzymes, yields phenyl-pyruvic acid and ammonia is released. This deamination is detected by the addition of a ferric chloride solution that acts as a chelating agent with the -keto acid by-product to produce a light to deep green cyclic compound.
- Phenylalanine agar, also known as phenylalanine deaminase medium which contains DL-phenylalanine and nutrients is used as a test medium.
- Hendriksen, in 1950, exhibited that Proteus spp. were able to convert phenyl- alanine to phenyl-pyruvic acid. This observation was integrated into a medium by Ewing et al. and into a disk along with urea by Ederer et al. . Of the Enterobacteriaceae that are urea positive, only members of the Proteus, Providencia, and Morganella group are capable of deaminating phenylalanine (2). The test can also be used to detect other Enterobacteriaceae, Buttiauxella, Rahnella, and Tatumella, which are PDA positive but are urea negative.
Requirements:
- Media: Phenylalanine agar slants:
- Contain L-phenylalanine and yeast extract in a buffered agar
- Store at 15 to 30°C.
- Reagents: 10% Acidified Ferric chloride
- Dissolve 12 g of ferric chloride in 97.5 ml of water.
- Slowly add 2.5 ml of concentrated HCl in a fume hood.
- tore in brown bottle at 4°C.
NOTE: Acidified ferric chloride is recommended, but 10% aqueous ferric chloride (10 g in 100 ml of de-ionized water) can be used.
- Apparatus:
- Inoculating loops
- Incubator at 35 to 37°C
- Distilled water
Procedure:
- Allow the medium to equilibrate to room temperature prior to inoculation.
- Streak the slant surface using a heavy inoculum from an 18- to 24-hr pure culture.
- Incubate the inoculated slant aerobically at 35°C for 18 to 24 h. If a heavy inoculum is used, incubate for 4 to 6 h.
- Apply 4 or 5 drops of ferric chloride directly to the slant after incubation.
- Gently roll the reagent over the slant to dislodge surface colonies, and observe for the development of a green colour within 1 to 5 min.
Results interpretation:
- Positive test: The progression of a light to dark green colour (PDA) or purple to black colour (TDA) within 1 to 5 min after the application of ferric chloride reagent is suggestive of a positive phenylalanine deamination reaction.
- Negative test: The absence of a green colour reaction is indicative of a negative test. Negative results will take on the yellow colour due to the colour of the ferric chloride.
