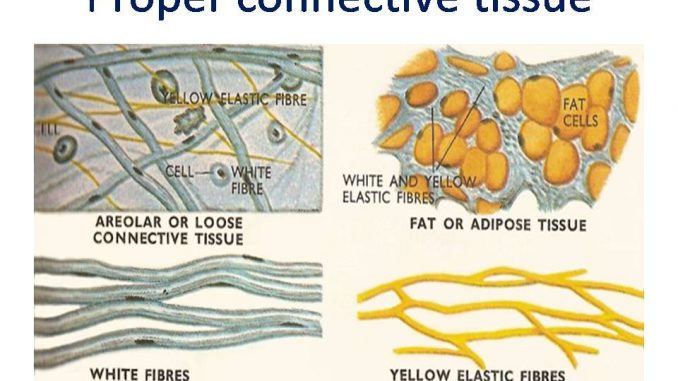
- In proper connective tissues, the matrix is soft, less rigid and shows varying degree of toughness.
- Accordingly the proper connective tissue have been divided into two types-loose and dense connective tissue
Types of proper connective tissue
I. loose connective tissue
II. Dense connective
I. Loose connective tissue:
- The cells in the matrix are widely distributed and the fibres are loosely woven.
- It generally connects and support various tissues and organs and helps them to resist strain and displacement.
- types-
- Areolar connective tissue
- Adipose connective tissue
- Reticular tissue
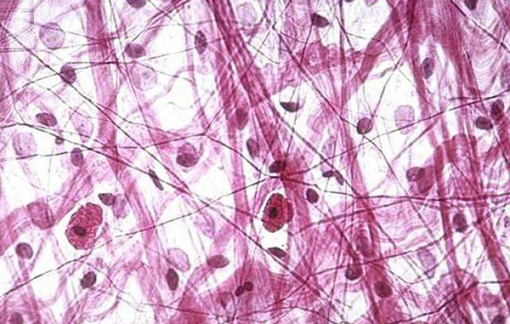
1. Areolar connective tissue:
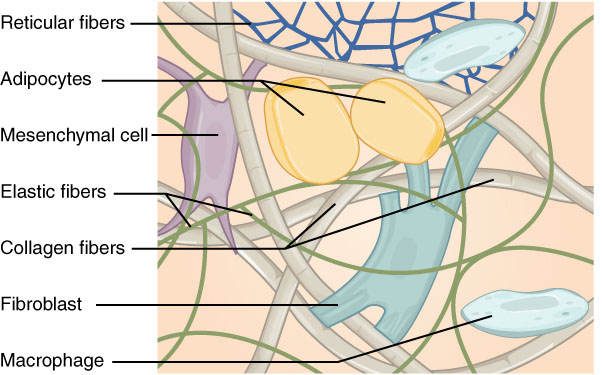
- These are simplest and most widely distributed connective tissues. It has homogenous, transparent, semi-fluid and gelatinous matrix. (glycoprotein, mucin, hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulphate).
- Matrix contain various types of cells (fibroblast, macrophages, mast cells, lymphocytes, fat cells, plasma cells) and fibres (white collagen fibres, yellow elastic fibres)
- Fibres are loosely arranged and there is space between fibres, areolae, which derives its name.
- Found in continuous layers beneath skin, space between many organs, between muscles, peritoneum and mesentries.
Functions:
- They binds tissues together
- They engulf bacteria and damaged and dead cells
- They secrete heparin and histamine. Heparin is an anticoagulant while histamine causes inflammation reaction
- They produces antibodies
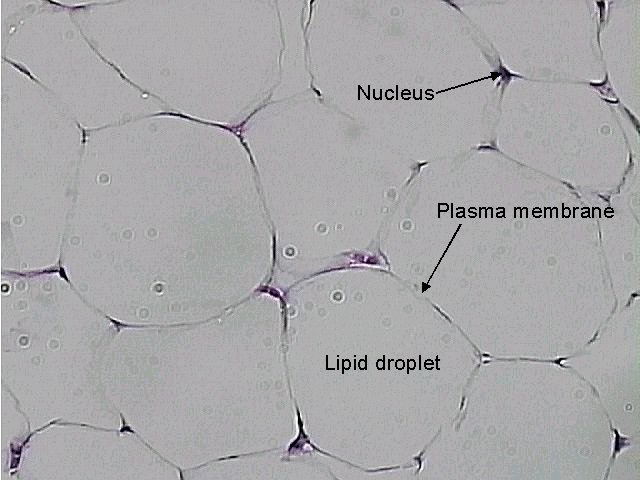
2. Adipose connective tissue:
- It is a modified form of areolar tissue that contain large number of fat cells ( Adipocytes cells).
- Adipocyte is a large, spherical or oval shaped cell, with large fat droplet causing shifting of nucleus to periphery of the cell
- 2 types of adipocytes- white adipocyte- contain a single large fat droplet and Brown adipocyte- contain number of small fat droplets
- Found beneath skin in dermis, mesentries, around kidney, heart and eye balls
Functions:
- As it synthesise, stores and metabolises fat, it is a considerable sourse of energy
- It acts as a shock absorbers around kidney, heart, and eye balls
- It prevent heat loss by forming insulating layer
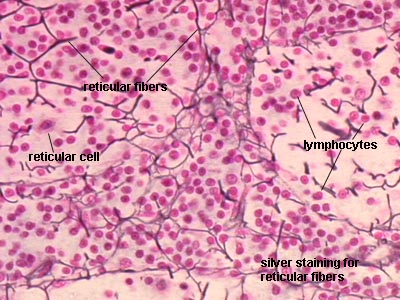
3. Reticular tissue:
- It is a modified areolar tissue that contains large number of stellate shape reticular cells floating in fluid matrix.
- Reticular cells has number of cytoplasmic processes which are interconnected to form reticular network.
- Reticular cells secretes reticular fibres
- Found-lymph glands, spleen, liver , bone marrow, thymus and tonsils.
Function:
- they are mostly phagocytic cells, helps in defense mechanism of the body
II. Dense (fibrous) connective tissue:
- The fibres dominate over the cells and the matrix in quantity.
- The fibres may be regularly or irregularly arranged
- types:
- White fibrous tissue ( tendon and sheath)
- Yellow elastic tissue (Ligament
1. White fibrous tissue:
- It contains fibroblast cells and collagen fibres and very few amount of matrix.
- The dense network of collagen fibres gives great strength.
- it occur in two form- i) tendon and Sheath
- Tendon is the thick bundle of collagen fibres running parallel to each other, giving strong, flexible but inextensible strength. It joins skeletal muscles to bones.
- Sheath is the bundles of collagen fibres lies in a criss-cross manner. It is present in pericardium of heart, dura matter, cornea, capsule of kidney, spinal cord. It also forms covering of cartilage and bones.
2. Yellow elastic tissue:
- These tissues contains numerous and closely packed yellow elastic fibres.
- Elastic fibre are long, straight and branched, they are elastic and flexible.
- They are present in Ligament, also present in wall of blood vessel, vocal cords, respiratory passage and lungs.
- Ligament– It is composed of yellow elastic fibres and some collagen fibres. It join two bone together.
