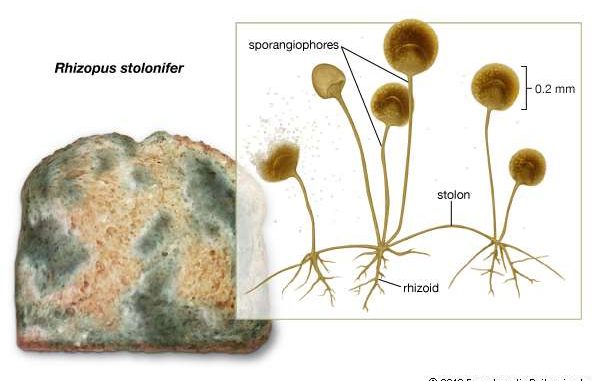
Rhizopus stolonifer: morphology and reproduction of black bread mold
- Rhizopus stolonifer is also known as black bread mold.
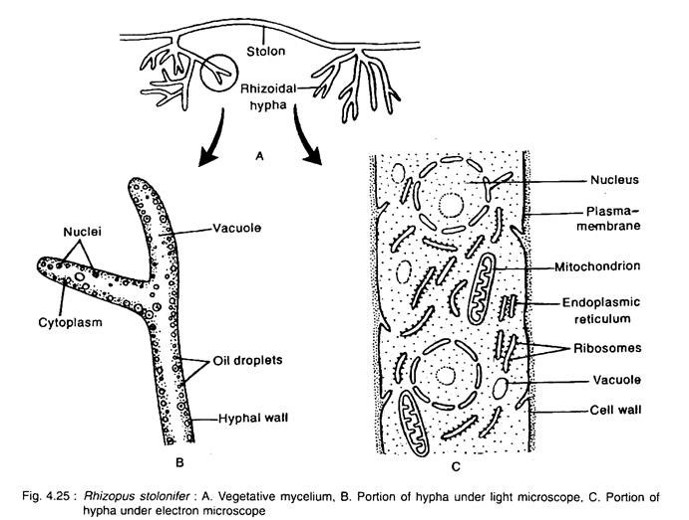
- Thallus is white cottony, much branched mycelium.
- Mycelium is differentiated into nodes and internodes. The nodal region bears much branched rhizoid grows downward, inside the substratum for anchorage and absorption of food.
- The internodal region is the aerial and arching hyphae, known as stolon, which when touches the substratum forms the nodal region
Reproduction in Rhizopus: life cycle
- Fragmentation
- Asexual method: Sporangiospore formation and chalmydospore formation
- Sexual method: gamentagial copulation
Fragmentation:
- Disjoining of hyphae gives new organism.
- It is one of the common mode of reproduction in Rhizopus
Asexual reproduction in Rhizopus:
- It occurs during favorable condition
- Aerial hyphae develop from internode and arise to certain height
- The nuclei and cytoplasm push more and more towards the apical side, consequently the apex of the aerial hyphae swells up.
- The swollen part enlarges and develops into a large round sporangium
- Sporangium differentiates into two region; multinucleated sporoplasm and vaculated columellaplasm
- Nucleus in sporoplasm divides rapidly, and each nuclei gather some cytoplasm and transform into spongiospore
- After maturity columella collapsed releasing sporangiospore in atmosphere
- Sporangiospore attached to substratum and germinates to give mycellium
- During unfavorable condition, septum formation occurs in mycelium and each intercalary mycelium give rise to thick resting spore known as chlamydospore.
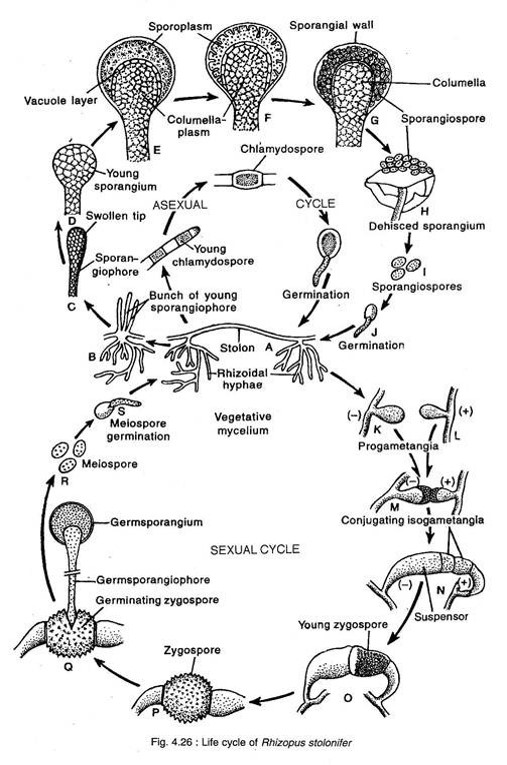
Sexual reproduction in Rhizopus:
- Sexual reproduction takes place during unfavourable condition by means of gametangial copulation.
- Most Rhizopus are heterothallic
- When two mycelium of opposite strain come close to each other, each mycelium produce small outgrowth, called progametangia
- The apical region of the two progametangia come in close contact and cytoplasm of each progametangium push more and more towards the apical region which swell up with dense protoplasm.
- The apical region is known as gametangia and basal region is known as suspensor
- The protoplasm in gametangia fuses to from zygospore
- Zygospore is a resting spore
- During favorable condition, spore wall rupture and form germ tube which elongates to form promycellium
- Promycellium have two region; germsporangiophore and germsporangium
- Nucleus in germsporanium divides by meiosis forming haploid nuclei, which gather cytoplasm and behaves as spore.
- The haploid spore are released and germinates to give mycellium
