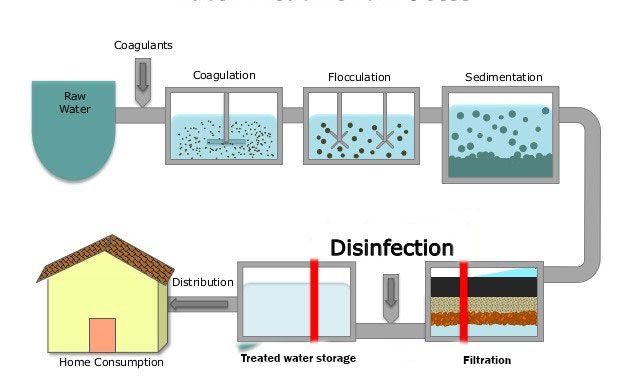
Steps of water purification process
- Detail step and methods of water treatment depends on nature of raw water and required standard of water quality.
General steps in purification of drinking water includes
1. Aeration:
- Raw water is first collected in large aeration tank and the water is aerated by bubbling compressed air through perforated pipes.
- Aeration removes bad odors and CO2. It also removes metal such as iron, manganese by precipitating then as their respective hydroxides.
2. Storage or settling:
- Aerated water is then placed in settling tank and stored for 10-14 days.
- During storage about 90% of suspended solids settle down within 24 hrs and the water becomes clear.
- Certain heavier toxic chemicals also settle down during storage.
- Similarly pathogenic bacteria gradually die and bacterial count decreases by 90% in first in first 5-7 days of storage.
- During storage organic matter present in water is oxidized by microorganisms. Similarly NH3 present is oxidized into nitrate by microorganisms during storage.
3. Coagulation:
- Water from storage tank is then placed in coagulation tank and then some precipitating agents such as alum, lime etc are added in water and mixed.
- These precipitating agents form precipitate of Al(OH)3 when dissolved in water.
- Suspended solids absorbs on the surface of precipitate, so gradually mass of precipitate becomes heavier and finally settle down.
- This technique is used to remove very light suspended solids that do not settle by themselves during storage. Furthermore, if negatively charged colloidal impurities are present, they are neutralized by Al+++ ions and settle down.
4. Filtration:
- Partially clarified water is then passed through sand gravity filter which removes 98-99% of microorganisms and other impurities.
- Sand gravity water filter:
- Sand filter is a rectangular tank in which filter bed is made up to 3 layers.
- Top layer: fine layer of 1 meter thick
- Middle layer: 0.3-0.5 meter thick layer of coarse sand
- Bottom layer: 0.3-0.5 meter thick layer of gravel
- There is a collection tank at the bottom of the filter bed to collect filtered water. During filtration filter bed soon gets covered with a slimy layer called vital layer.
- Vital layer consists of thread like algae, diatoms and bacteria.
- During filtration microorganisms presents in vital layer oxidize organic and other matter present in water. For example if NH3 is present, it is oxidized into nitrate.
- Vital layer also helps in filtration of microbial cells.
- If water contains unpleasant odor, activated carbon may be placed in filter bed that removes bad odors.
5. Disinfection:
- The filtered water is finally purified by using disinfectants. Eg. Chlorination
- Disinfectant kills pathogenic as well as other microorganism in water.
- After disinfection water is pumped into overhead tank for subsequent domestic distribution.
