T-lymphocyte: types and functions
- T-cells originate in bone marrow and mature and differentiate in thymus. The name T- cells is derived from its site of maturation.
- All T-cells contains T- cell receptor (TCR) on its surface. TCR is specific and recognize MHC bound antigen.
- All T- cells expresses an antigen binding TCR and CD2 and CD3 glycoprotein on their cell membrane.
- Most of the T-cells are distinguished on the basis of CD4 and CD8 glycoprotein receptor on their cell membrane.
- CD4 T- cell: those T- cells which contains CD4 glycoprotein on its surface in addition to TCR, CD2 and CD3. CD4+T-cells recognize antigen bound to MHC-II.
- CD8 T-cell: those T cells which contains CD8 glycoprotein on its surface in addition to TCR, CD2 and CD3. CD8+ T-cellsrecognize antigen bound to MHC-I
- None of the T- cells contains both CD4 and CD8, similarly, non T- cells lack both CD4 and CD8 glycoprotein receptor on its surface.
- Other membrane receptors on surface of mature T- cells are:
- CD28; a receptor for co-stimulatory B7 or for Antigen presenting cells (APC)
- CD45; a signal transduction molecule
Functional sub-population of T-cells:
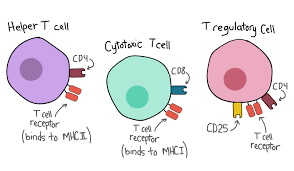
i. Helper T-cells (TH) or CD4+ T -cells
- TH cells are activated by recognition of antigen on MHC-II on APCs. Ie. MHC-II restricted.
- When antigen binds on TCR of CD+ T –cells, it is activated and divides into memory cell and effector cells. Effector TH cells secretes various cytokines which helps in B-cell activation for production of antibodies.
ii. Cytotoxic T-cells (Tc) or CD8+ T –cells:
- Tc cells are activated by recognition of antigen on MHC-I on altered self cell such as tumor cell or virus infected cells.. Ie. They are MHC-I restricted.
- When antigen binds on TCR of CD8+ cells, it is activated and divides into clones of memory cell and effectors cells. Effector Tc cells is known as cytotoxic T-lymphocytes (CTL) which kills virus infected cell or tumor cells.
iii. Supressor cells (Ts-cells):
- Ts-cells helps to suppress humoral and cell mediated immunity.
Immunological functions of T-lymphocytes:
- Helps B- cell maturation, expression and antibody production
- Helps in recruitment and activation of mononuclear phagocytic cells.
- Helps in recruitment and activation of specialized cytotoxic T- cells (TCL) in antiviral response.
- Secretes cytokines which is responsible for growth and differentiation of T- cells, monocytes, macrophages etc
- Helps in regulation of immune reactions.
