
Three point test cross
Three point test cross in Drosophila:
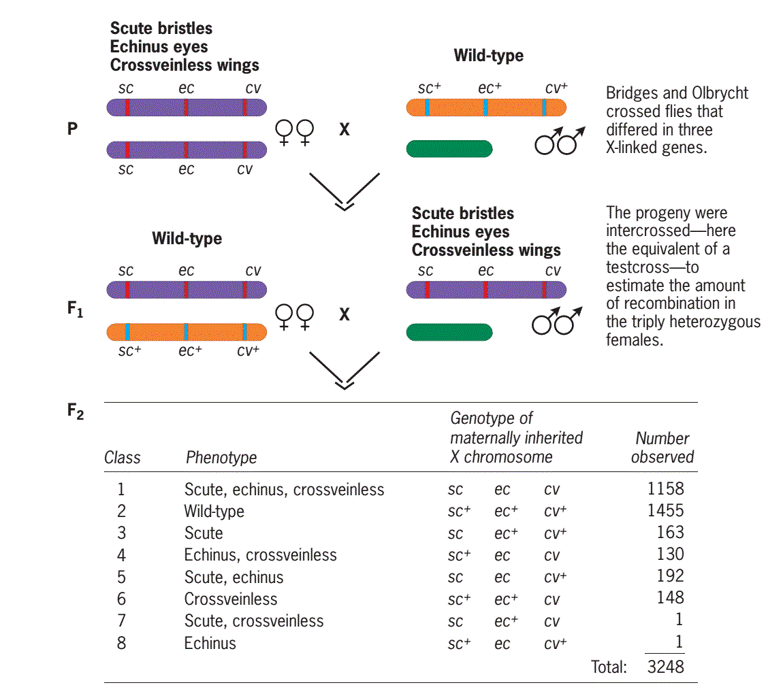
- Wild-type Male Drosophila was crossed with female Drosophila homozygous for three recessive X-linked mutations—scute (sc) bristles, echinus (ec) eyes, and crossveinless (cv) wings to obtain F1 progeny.
- Wild Male Drosophila= (sc+, ec+, cv+)
- Mutated female Drosophila = (sc, ec, cv)
- Then F1 progeny were intercrossed to produce F2 flies, which are then classified and counted.
- The F1 males carried the three recessive mutations on their single X chromosome. Thus, this intercross was equivalent to a testcross with all three genes in the F1 females present in the homozygous form.
- The F2 progeny flies from the intercross comprised eight phenotypically distinct classes, two of them are parental and six recombinant.
| Class | Phenotypes | Characters | Genotypes | Counts |
| 1. | Scute, echinus, crossveinless | Parental | Sc, ec, cv | 1158 |
| 2. | Wildtype (non scute, non echinus, crossvein) | Parental | Sc+, ec+, cv+ | 1455 |
| 3. | scute | Recombinant | Sc, ec+, cv+ | 163 |
| 4. | Echinus, crossveinless | Recombinant | Sc+, ec, cv+ | 130 |
| 5. | Scute, echinus | Recombinant | Sc, ec, cv+ | 192 |
| 6. | Crossveinless | Recombinant | Sc+, ec+, cv | 148 |
| 7. | Scute, crossveinless | Recombinant | Sc, ec+, cv | 1 |
| 8. | echinus | Recombinant | Sc+, ec, cv+ | 1 |
| Total | 3248 | |||
Gene order:
- The parental classes were by far the most numerous (1158+1455=2613). The less numerous recombinant classes each represented a different kind of crossover chromosome.
- To figure out which crossovers were involved in producing each type of recombinant, we must first determine how the genes are ordered on the chromosome.
- There are three possible gene orders :
- sc—ec—cv
- ec—sc—cv
- ec—cv—sc
- Four of the recombinant must have come from a single crossover in one of the two regions of the genes. The other two recombinant must have come from double crossing over—one exchange in each of the two regions. Because a double crossover switches the gene in the middle with respect to the genetic markers on either side of it, it is used for determining the gene order.
- Again, intuitively, double crossover occur much less frequently than a single crossover. Therefore, among the six recombinant classes, the two rare ones must represent the double crossover chromosomes
- From the given example, the double crossover must have occurred in class 7 (sc ec+cv) and class 8 (sc+ec cv+), each containing a single recombinant F2 progeny.
- Comparing these rare recombinant to parental class 1 (sc ec cv) and class 2 (sc+ec+Cv+), the echinus allele has been switched with respect to scute and crossveinless.
- Consequently, the echinus gene must be located between the other two.
- Therefore the correct gene order is sc–ec–cv.
Map distance:
- It is the distance between each pair of gene and it is obtained by estimating the average number of crossovers.
- Total map distance between these three genes is map distance between sc and ec plus map distance between ec and
i. Map distance between sc and ec:
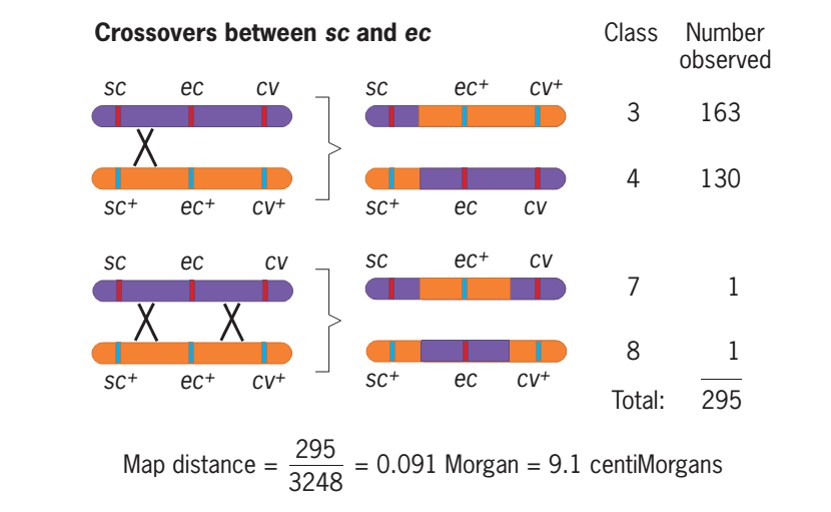
- We can obtain the length of the region between sc and ec by identifying the recombinant classes that involved a crossover between these genes.
- There are four such classes: class 3 (sc ec+cv+), class 4 (sc+ec cv), class 7 (sc ec+cv), and class 8 (sc+ec cv+).
- Classes 3 and 4 involved a single crossover between sc and ec, and classes 7 and 8 involved two crossovers, one between sc and ec and the other between ec and
- We can therefore use the frequencies of these four classes to estimate the average number of crossovers between sc and ec:
- Average crossover between sc and ec =(163+130+1+1) /3248
=0.091 Morgan
=9.1 centiMorgan or Map unit
- Thus, in every 100 chromosomes coming from meiosis in the F1 females, 9.1 had a crossover between sc and ec.
- The distance between these genes is therefore 9.1 map units.
ii. Map distance between ec and cv:
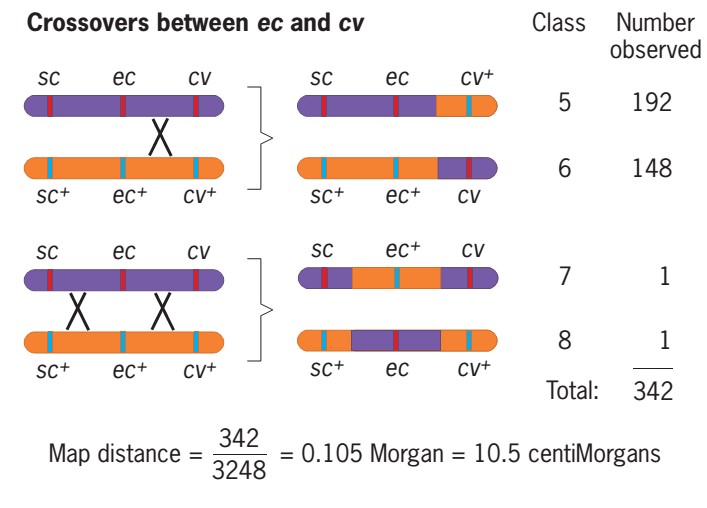
- In a similar way, we can obtain the distance between ec and cv.
- Four recombinant classes involved a crossover in this region: class 5 (sc ec cv+), class 6 (sc+ec+cv), class 7 and class 8.
- The double recombinants are also included here because one of their two crossovers was between ec and cv.
- The average cross between ec and cv =(192+148+1+1)/3248
=0.105 morgan
= 10.5 centiMorgans or map unit
Total map distance:
- Combining the data for the two regions, the map is sc—9.1— ec—10.5— cv
- Thus map distances between sc and cv= 9.1 cM +10.5 cM =19.6 cM
Alternative way of calculating map distance:
- Directly calculating the average number of crossovers between these genes:
- Recombination frequency (RF)= Non–crossover + Single crossover + Double crossover
= (0)*(1158+1455)/3248 + 1 (163+130+192+148)/3248 + 2 (1+1)/3248
= 0 + 0.195 + 0.0006
= 0.196 Morgan
= 19.6 CentiMorgan
Inference and coefficient of coincidence:
- Inference is the phenomenon of inhibition of crossover of by another crossover nearby.
- For example, the crossover frequency between sc and ec in region I was (163 +130 +1+1)/3248 =0.091, and crossover frequency between ec and cv in region II was (192+148 +1 +1)/3248 =0.105.
- If we assume both crossover are independence of each other, the expected frequency of double crossovers in the interval between sc and cv would be 0.091 *0.105 = 0.0095.
- But actual observed frequency of double crossover is (1+1)/3248 = 0006
- Double crossovers between sc and cv were much less frequent than expected.
- The result suggest one crossover inhibited the occurrence of another nearby, a phenomenon called interference
- The extent of the interference is measured by the coefficient of coincidence (C).
- Coefficient of coincidence is the ratio of observed frequency to double cross to expected frequency to double cross.
- C= (observed frequency of double crossovers)/(expected frequency of double crossovers)
=0.0006/0.0095
C=0.063
Level of inference (1-C):
- Level of inference = 1-C
- =1-0.063
- =0.937
- Because in this example the coefficient of coincidence is close to zero, its lowest possible value, interference was very strong (I is close to 1).
- cases:
- if a coefficient of coincidence equal to 1; no interference between crossover at all which means the crossovers occurred independently of each other.
- If a coefficient of coincidence is equal to 0; very strong inference between crossover therefore double cross do not occur.
- ** map distance less than 20cM has very strong inference. Thus, double crossovers seldom occur in short chromosomal regions.
- The strength of interference is therefore a function of map distance
