
Transduction: generalized and specialized transduction
- Transduction is a method of gene transfer in bacteria from donor to recipient using bacteriophage.
- In transduction at first bacteriophage infects donor bacteria and then carries some part of donor genome with it. When this bacteriophage infects new bacterial cell, it transfer that DNA in to recipient cell.
There are two types of transduction
- Generalized transduction
- Specialized transduction
1. Generalized transduction:
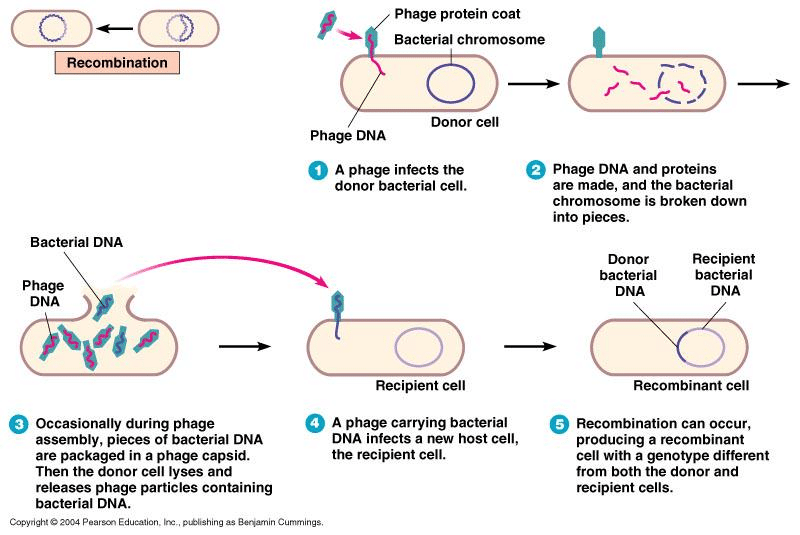
- If all the fragments of donor DNA from any region of chromosome have a chance to enter into transducing bacteriophage then it is known as generalized transduction.
- In this type of transduction, at first bacteriophage infects donor cell and begins lytic cycle.
- When virus enter into bacterial cell, virus hijack host cell and synthesize virus components such as genome, enzymes, capsid, head tail and tail fibers. Then viral enzyme hydrolyses host cell DNA into small fragments.
- During assembly of virus component to form progeny viruses, sometime any of the fragments of donor DNA get incorporated into the virus capsid (bacteriophage head). Such abnormal bacteriophage when infects a new cell, it can transfer this donor DNA into new bacteria. Since this donor DNA is not viral DNA, it does not replicates inside recipient bacteria but undergoes homologous recombination with recipient cell’s chromosomal DNA forming recombinant cell.
2. Specialized transduction:
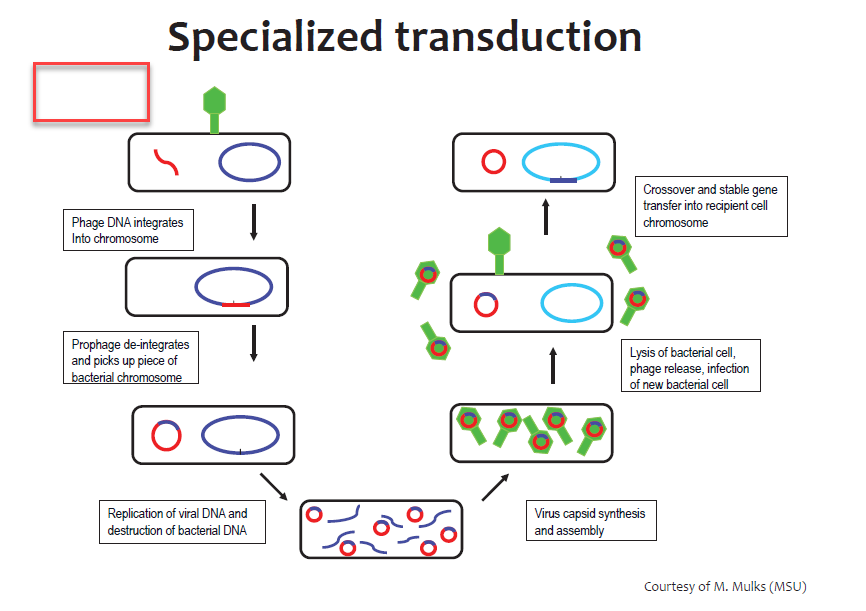
- In specialized transduction, bacteriophage transfer only a few restricted gene (DNA fragments) from donor bacteria to recipient bacteria. Specialized transduction is carried only by temperate bacteriophage which undergoes lysogenic cycle in donor cell.
- At first temperate bacteriophage enter into donor bacteria and then its genome gets integrated with host cell’s DNA at certain location and remains dormant and pass generation to generation into daughter cell during cell division. The bacteriophage which follows lysogenic cycle is known as temperate phage.
- When such lysogenic cell is exposed to certain stimulus such as some chemicals or UV lights, it causes induction of virus genome from host cell genome and begins lytic cycle.
- On induction from donor DNA, this phage genome sometimes carries a part of bacterial DNA with it. The bacterial DNA lies on sides of integrated phage DNA are only carried during induction.
- When such bacteriophage carries a part of donor bacterial DNA infects a new bacteria, it can transfer that donor DNA fragments into new recipient cell. So, in this specialized transduction only those restricted gene are situated on the side of integrated viral genome have a chance to enter into recipient cell.

I real appreciated your notes are so readable as well as understandable