
- Vitamin E is also termed as anti-sterility vitamin
- It is a very powerful biological antioxidant.
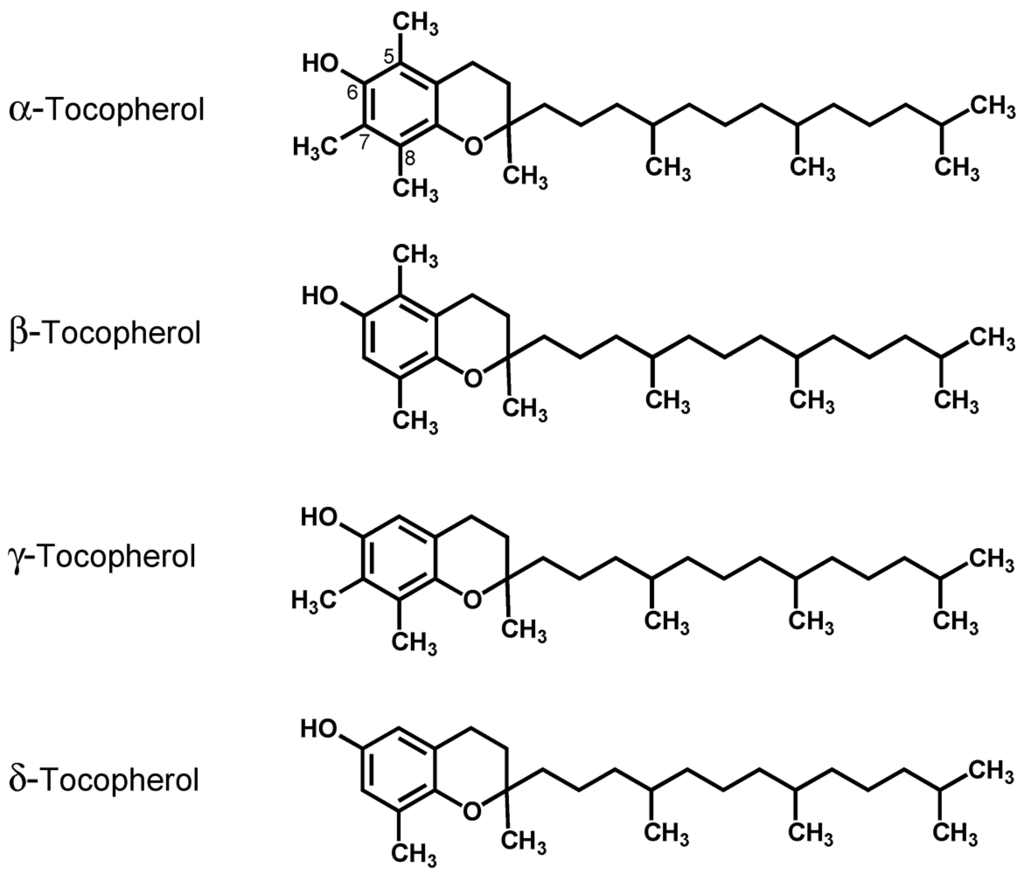
- It is a common term for a group of closely related lipids called as tocopherols.
- It is also called as vitamin in search of disease. It is because disease associated with its deficiency is yet unknown.
- Some of the common forms of Vitamin E are as follows:
α-tocopherol = 5,7,8-trimethyltocol
β-tocopherol = 5,8-dimethyltocol
γ-tocopherol = 7,8-dimethyltocol
- 𝛿-tocopherol= 2,8-dimethyltocol
- Vitamin E is observed in presence of bile salt from the intestine.
- It is incorporated into lipoproteins, LDL and VLDL and stored in muscles, liver and adipose tissue.
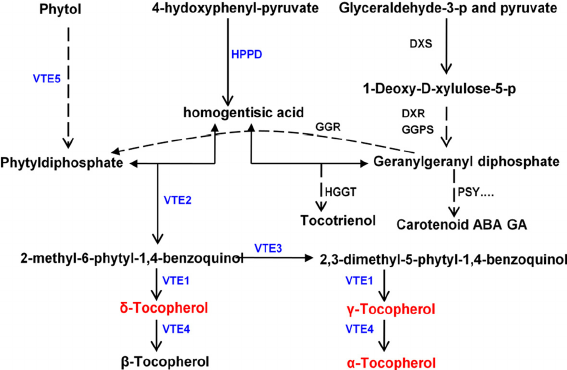
Biosynthesis of Vitamin E:
Biological roles of vitamin E:
- The major functions of vitamin E are confined to flowing aspects:
- Maintenance of normal cell membrane:
- Vitamin E is responsible for maintaining the integrity of cell membrane by preventing the oxidation of polyunsaturated fatty acid by the effect of super-oxides, peroxide and other free radicals.
- Vitamin E prevents the hemolysis of RBCs by preventing the oxidation of unsaturated fatty acids in erythrocytes membrane.
- Role in metabolism:
- Vitamin E have been found involved in synthesis of nucleic acid.
- It is also engaged in storage of keratin in membrane and absorption of aminoacids in intestine.
- Reproduction:
- Vitamin E is an anti-sterility vitamin.
- It maintains the normal germinal epithelium of the gonads.
- Prevention of cataract and heart disease:
- Vitamin E prevent the oxidation of vitamin A (
-carotene).
- Therefore, prevent the risk of cancer associated with the free radicals, super-oxides, peroxides.
- Vitamin-E along with A and C is involved in the prevention of cataract and heart disease.
- Vitamin E prevent the oxidation of vitamin A (
- Heme synthesis:
- Vitamin E is required for the activity of delta-aminolevulinic acid which is required for the synthesis of Heme from the condensation of glycine and succinyl coA.
- Role in respiration:
- Co-enzyme Q (Ubiquinone) in membrane is stabilized by vitamin E and therefore aids in cellular respiration.
Recommended dietary allowance (RDA) of vitamin E:
- RDA value is 10mg/day (15 IU) in male.
- RDA value is 8mg/day (12 IU) in female.
- Higher intake is required during pregnancy and lactation.
Dietary sources of Vitamin E:
- Vegetables are rich source in vitamin E.
- Wheat germ oil, peanut oil, soyabean oil, corn oil, cotton seed oil, are rich source of Vitamin E.
- Butter, milk, meat, egg are also sources of Vitamin E.
Deficiency of vitamin E:
- Vitamin E as mentioned earlier is called as vitamin in search of disease.
- Due to deficiency of vitamin E in humans, fragile erythrocytes, abnormal cell membrane and minor neurological sign are observed.
- In cases of mature female rats, sterility is observed whereas in male rats, the germinal epithelium of testes degenerates and spermatozoa becomes non-motile.
Hypervitaminosis E:
- There is no any hypervitaminosis cases associated with Vitamin E.
