Parathyroid gland: structure, location and Hormones
Structural anatomy of Parathyroid gland
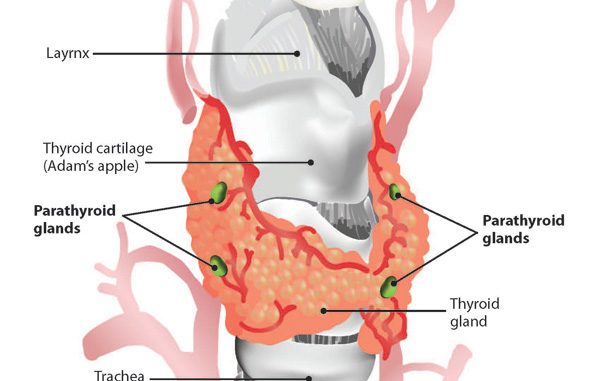
- Parathyroid glands are tiny, lentil sized gland embeded in posterior of thyroid gland.
- two pairs of parathyroid glands are found.
- each thyroid lobe contains two parathyroid gland.
- The gland is composed of principal cells (secrete parathormone) and Oxyphilic cells (store parathormone)
Location: embedded on posterior of thyroid gland
Size: small lentil sized, 4 in number
Hormones of Parathyroid gland
-
Parathormone
- Regulate the concentration of calcium and phosphate level in blood
- Increase level of Ca++ in blood by reabsorption from intestine and kidney, Osteolysis
- Low Ca++ concentration in blood stimulate parathormone synthesis.
- Promote decalcification and demineralization of bone.
- stimulates Osteoclast to break (Osteolysis) to release Calcium from bone to blood.
* Improper balance of calcium and phosphate in blood causes faulty nerve impulse transmission, destruction of bone tissue, hamper bone growth and muscle tetany.
** when calcium level increases in blood, parathormone stimulates inhibition of reabasorption of calcium in kidney and inhibit osteolysis of bone.
Disorder of Parathyroid gland:
1. Parathyroid tetany:
- deficiency of parathormone
- muscle spasms, sustained contractions of muscles
- may leads to death
2. Osteoporosis:
- over secretion of parathormone
- decalcification of bones
- bone becomes soft and porous
