
Xanthoproteic test: Objective, Principle, Reagents, Procedure and Result
Objective:
- this test is used to differentiate aromatic amino acids which give positive result from other amino acids
Principle:
- Xanthoproteic test is used to detect amino acids containing an aromatic nucleus (tyrosine, tryptophan and phenylalanine) in a protein solution which gives yellow color nitro derivatives on heating with conc. HNO3. The aromatic benzene ring undergoes nitration to give yellow colored product. Phenylalanine gives negative or weakly positive reaction though this amino acid contains aromatic nucleus because it is difficult to nitrate under normal condition. On adding alkali to these nitro derivative salts, the color change fro yellow to orange.
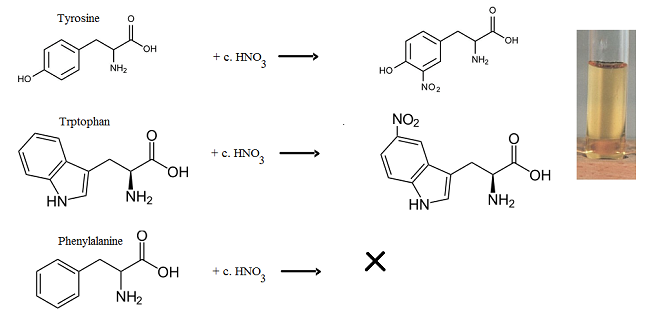
Reactions:

Reagents:
- test solution: 1 % tyrosine, 1 % tryptophan, 1 % phenylalanine, 5 % egg white (albumin)
- Nitric acid
- 40 % NaOH
Procedures
- Take 1ml test solution in dry test tube.
- Similarly, take 1ml distilled water in another test tube as control.
- Add 1ml of conc. HNO3 in all test tubes and mix well.
- Cool the solution under tap water.
- Now add 2ml of 40 % NaOH to all test tubes.
- Look for the color development.
Result:

